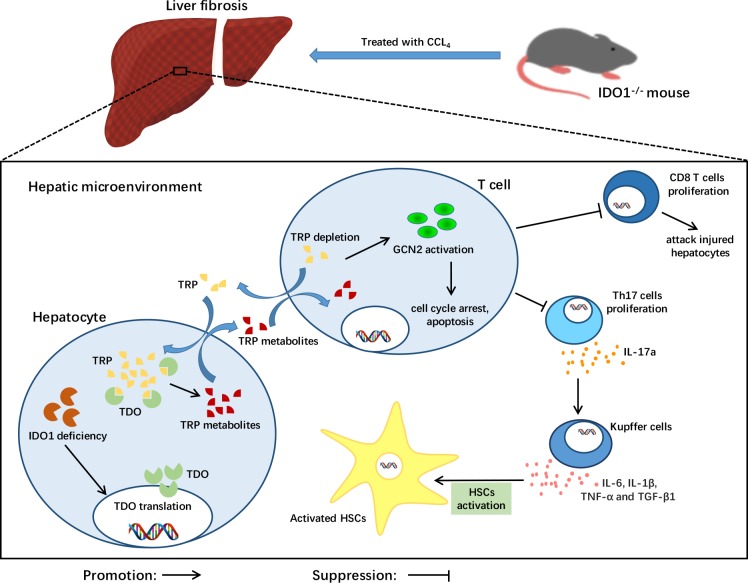
Figure 6. A model depicting the key role of IDO1 deficiency in the pathogenesis of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis.
After treatment with CCl4, TDO in liver was increased under the condition of IDO1 deficiency. The compensation of TDO can degrade TRP, the depletion of which activates GCN2 kinase, subsequently suppressing the proliferation of both CD8+ cells and Th17 cells. Liver lesions are ameliorated due to less hepatocyte damage induced by CD8+ cells. HSCs can be activated by cytokines, including IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α and TGF-β1, that are secreted by Kupffer cells under stimulation with Il-17a. Consequently, IDO1 deficiency protects mice from CCl4-induced fibrosis mediated by Th17 cells and TDO compensation.