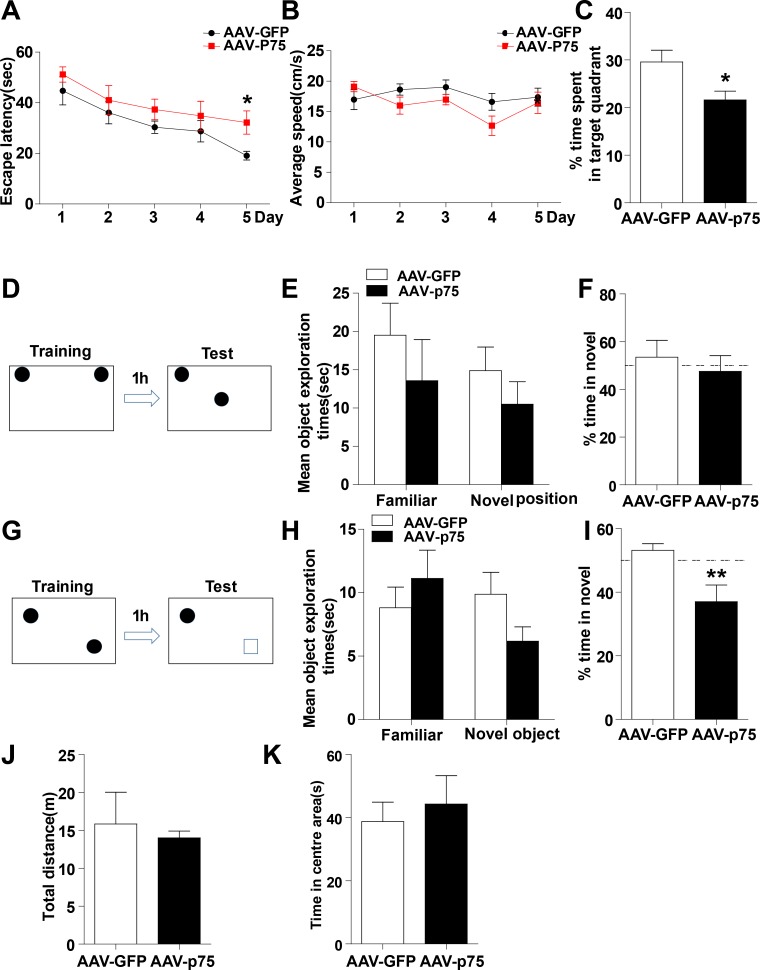
Figure 2. Intrahippocampal infusion of AAV-p75 in normal rats reproduce the cognitive deficits.
(A-C) Morris water maze test. Comparison of the escape latencies (A), mean swimming speed (B) and the percentage of target quadrant exploring time in probe test (C) between the AAV-GFP and AAV-P75 groups. (D-F) Object location recognition test. Diagram of the object location recognition task (D); The graph shows the object exploration during the test phase (E); Both AAV-GFP and AAV-p75 rats spent more time exploring a novel object location (F). (G-I) Novel object recognition test. Diagram of the object recognition task (G); The graph shows the object exploration during the 5 min test phase (H); The AAV-p75 rats did not display any preference for an object placed to a novel object (I). (J-K) Open field test. No significant differences were detected in total distance travelled test (J), and percent time travelled in the centre of the open files (K) between AAV-GFP and AAV-p75 groups. All data are presented as mean ±SEM. *p<0.05; **p<0.01. n= 10-15/group.