Figure 5. Treatment with PR5-LL-CM01 significantly inhibited NF-κB activation in PDAC and CRC cells.
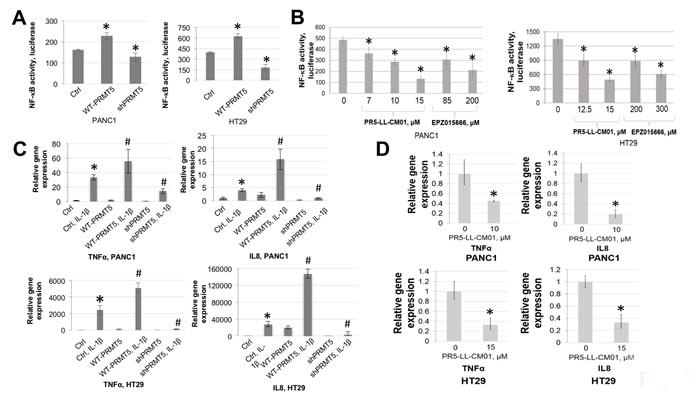
A. NF-κB luciferase assay, showing that overexpression of WT-PRMT5 led to NF-κB activation, while shPRMT5 resulted in quite opposite effect in both PANC1 and HT29 cells. *P < 0.05 vs. Ctrl. B. Luciferase assay, showing a decrease in NF-κB activation with increasing concentrations of PR5-LL-CM01 in PANC1 (left panel) and HT29 cells (right panel). A much higher concentration of EPZ015666 is needed in order to reach similar level of NF-κB inhibition as that of PR5-LL-CM01. The data represent the means ± S.D. for three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. Untreated group. C. qPCR analysis, showing that overexpression of PRMT5 significantly enhanced IL-1β-triggered NF-κB target genes (TNFα and IL8) expression, while shPRMT5 exhibited quite opposite effect, in both PANC1 and HT29 cells. *P < 0.05 vs. Ctrl; #P < 0.05 vs. Ctrl+IL-1β-treated group. D. qPCR analysis, showing that treatment with PR5-LL-CM01 dramatically decreased TNFα and IL8 expression, in both PANC1 and HT29 cells. The data represent the means ± S.D. for three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. Untreated group.
