Figure 1. Regulating chromatin conformation: The two faces of DICER.
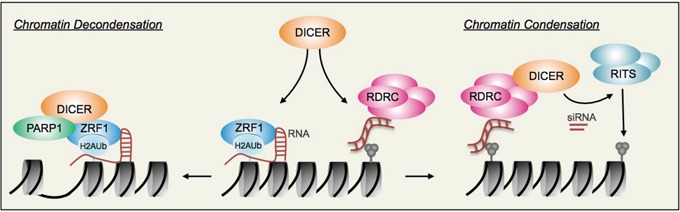
DICER facilitates chromatin decondensation by assembling with ZRF1 and PARP1. ZRF1 tethers to chromatin that is mono-ubiquitylated at lysine 119 of histone H2A and RNA species contribute to ZRF1 occupancy at chromatin. ZRF1 provides a binding platform and recruits DICER to chromatin. Multiprotein complexes consisting of DICER, ZRF1, PARP1 and potentially proteins from the family of SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complexes cause a local decondensation of chromatin. Further, DICER assembles with RNA-dependent RNA polymerase complexes (RDRC) and facilitates chromatin condensation by targeting RITS complexes to chromatin thereby spreading H3K9 methylation (H3K9me3; grey balls) to silence chromatin. For details refer to [3].
