Figure 3.
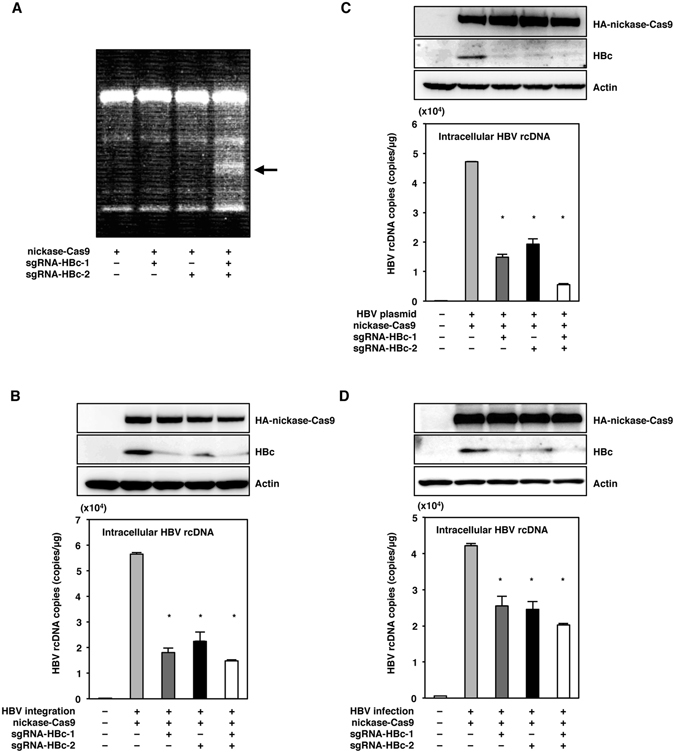
The expression of nickase-Cas9 with either or both of the sgRNAs suppressed the replication of HBV. (A) Nickase-Cas9 with sgRNA-HBc-1 and/or sgRNA-HBc2 was lentivirally transduced in HepG2.2.15.7 cells. Total DNA was collected at 5 days post-transduction, and mutations of HBV genome in HepG2.2.15.7 cells were detected by surveyor assay. The arrow indicated the surveyor digestion product. (B) HepG2.2.15.7 cells transduced with nickase-Cas9 and the sgRNAs were collected at 5 days post-transduction, and the expression of HBc was determined by immunoblotting. Intracellular HBV rcDNAs were extracted at 5 days post-transduction and quantified by qPCR. (C) Huh7 cells transduced with nickase-Cas9 and the sgRNAs were transfected with a plasmid containing 1.3-fold-overlength genome of HBV at 3 days post-transduction. Cell lysates were collected at 3 days post-transfection, and the expression of HBc was determined by immunoblotting. Intracellular HBV rcDNAs were extracted at 3 days post-transfection and quantified by qPCR. (D) HepG2-hNTCP-C4 cells expressing nickase-Cas9 and the sgRNAs by lentivirus vector were infected with HBV derived from the supernatants of HepAD38.7 cells at 3 days post-transduction. Cell lysates were collected at 10 days post-infection, and the expression of HBc protein was determined by immunoblotting. Intracellular HBV rcDNAs were extracted at 10 days post-infection and quantified by qPCR. *p < 0.01 vs. the results for control cells. (full-length gels are presented in Supplementary Figure).
