Figure 2.
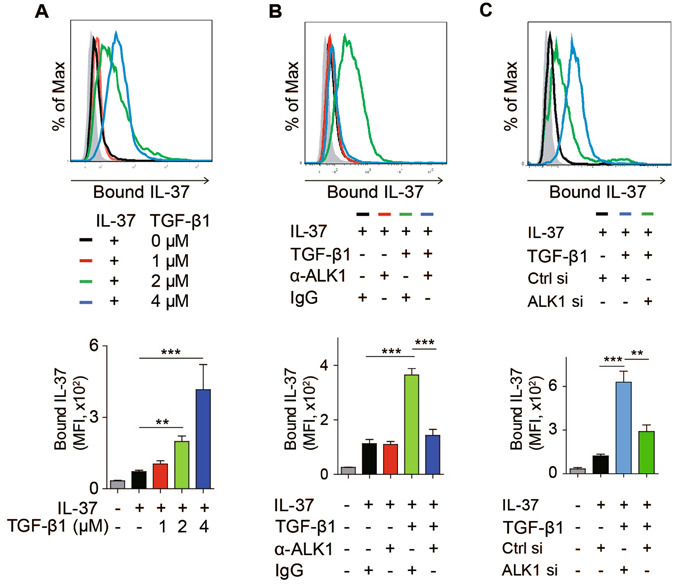
TGF-β1 enhanced the binding of IL-37 to HUVECs. (A) TGF-β1 facilitates the binding of IL-37 to HUVECs. HUVECs were incubated with 1 μM biot-IL-37 with/without indicated concentrations of TGF-β1. Bound biot-IL-37 was assessed by flow cytometry. Gray histograms indicated unlabeled cells. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of bound IL-37 was quantified (n = 4). (B) ALK-1 mediates TGF-β-facilitated binding of IL-37 to HUVECs. Flow cytometry of HUVECs incubated with indicated cytokines or antibodies. Biot-IL-37 and TGF-β1 were used at 1 μM. Anti-ALK1 antibody (α-ALK1) and IgG were used at 10 μg/mL. (C) Control and ALK1 siRNA-transfected HUVECs were incubated with indicated proteins or antibodies (10 μg/mL). Biotinylated IL-37 (biot-IL-37) and recombinant TGF-β were used at 1 μM. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
