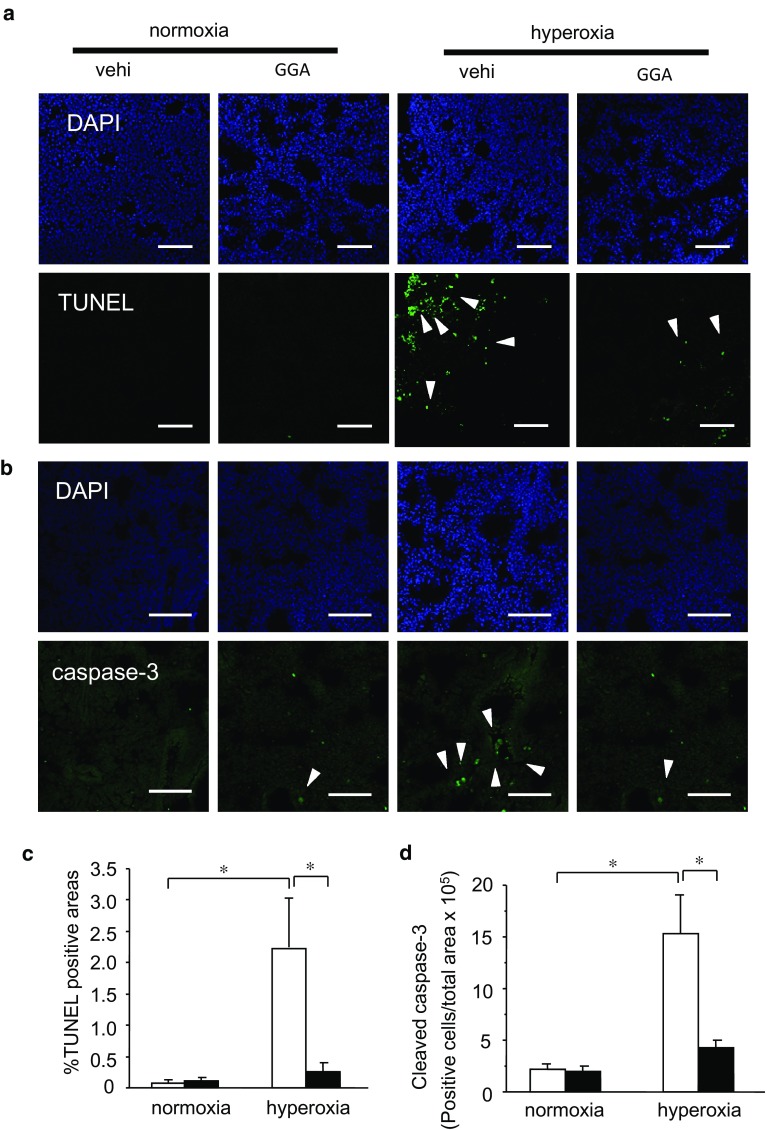
Fig. 4.
GGA treatment inhibited hyperoxia-induced apoptosis in lungs. Nucleus and apoptotic cells were identified via DAPI staining and the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) method (a), and cleaved caspase-3 immunohistochemistry (b) in the hyperoxia-exposed neonatal lungs treated with 500 mg/kg GGA or vehicle alone. TUNEL-positive areas (c) and cleaved caspase-3-positive cells (d) expressed per the total area of the lung section of each slide were compared between the vehicle-treated group (open bars) and the GGA-treated group (closed bars) under normoxia or hyperoxia. Arrows indicate TUNEL-positive cells (a) and cleaved caspase-3-positive cells (b). All images at ×200 magnification. Scale bar: 100 μm. Data are the mean ± SEM (normoxia/vehicle group: n = 6; normoxia/GGA group: n = 6; hyperoxia/vehicle group: n = 7; hyperoxia/GGA group: n = 6). Comparison between the indicated groups (*p < 0.05)