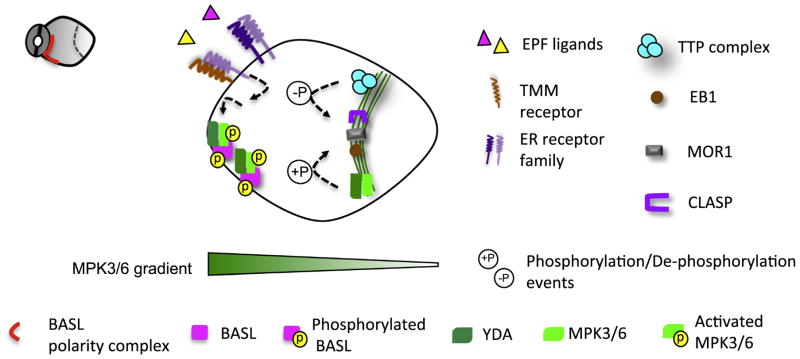
Fig 3.
A hypothetical MAPK gradient and asymmetric placement of cell division plane in the Arabidopsis stomatal lineage. In Arabidopsis stomatal ACD, we hypothesize that the YDA MPK3/6 signaling forms a gradient. Two possible mechanisms may contribute to this gradient. The positive feedback loop with BASL maintains a high concentration of MPK3/6 at the crescent. Extrinsic peptide ligands EPF1/2, derived from the neighboring stomatal cells, are perceived by the membrane receptors TMM and ERECTA family, which may locally activate the downstream YDA-MPK3/6 pathway. The formation of the PPB requires a core TTP complex containing protein phosphatase PP2A enzymes with two MT-binding proteins, TON1 and TRM. The PPB-associated MT regulators, e.g. MOR1, CLASP1 and EB1, might be subject to MAPK- and PP2A-mediate phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, respectively, to initiate and orientate the PPB formation.