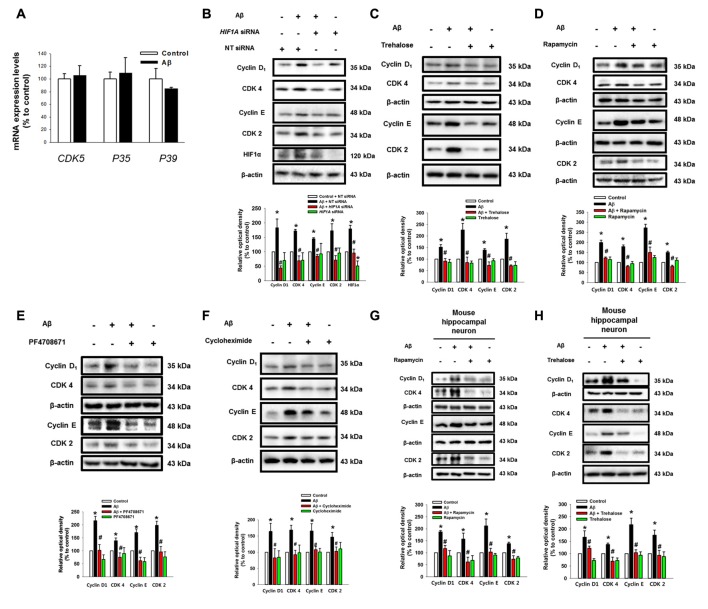
Figure 5.
Aβ induces the expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins. (A) SK-N-MC cells were exposed to Aβ (5 μM) for 24 h. The mRNA expression levels of CDK5, P35 and P39 were analyzed by real-time PCR. The mRNA expression level was normalized by β-actin mRNA expression level. Data represent the mean ± SE. n = 4. (B) hif1α specific- and non-targeting (NT) siRNA were transfected to the cells for 24 h prior to Aβ treatment. Cyclin D1, CDK4, cyclin E, CDK2, HIF1α and β-actin was detected by western blot. n = 3. (C–F) Cells were pretreated with trehalose (10 μM), rapamycin (10 nM), PF4708671 (10 μM) and cycloheximide (4 μM) for 30 min prior to Aβ treatment for 24 h. Cyclin D1, CDK4, cyclin E, CDK2 and β-actin were detected by western blot. n = 3–6. (G) Mouse hippocampal neurons were transfected with hif1α specific- and NT siRNAs for 24 h prior to Aβ treatment for 24 h. Samples were blotted with Cyclin D1, CDK4, cyclin E, CDK2 and β-actin specific antibodies. n = 3–6. (H) Mouse hippocampal neurons were pretreated with trehalose (10 μM) for 30 min and incubated with Aβ for 24 h. cyclin D1, CDK4, cyclin E, CDK2, HIF1α and β-actin were analyzed by western blot. n = 3–6. Data are presented as a mean ± SE. *p < 0.05 vs. control, #p < 0.05 vs. Aβ treatment.