Figure 8.
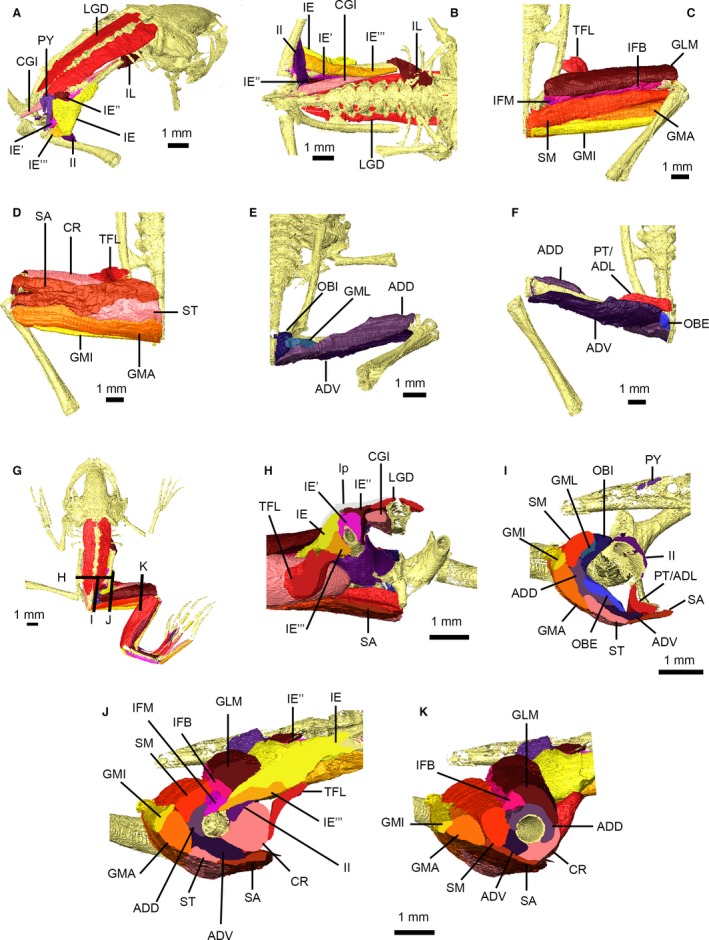
Pelvic and thigh musculature of Xenopus laevis. Pelvic musculature in right dorsolateral (A) and ventral (B) views with the ligamentous plate removed. Superficial (C,D) and deep (E,F) thigh muscles in dorsal (C,E) and ventral (D,F) views. Dorsal view of specimen (G) showing location of cross‐sections through the pelvis (H) and thigh (I–K). Muscles are identified using uppercase abbreviations; non‐muscle structures are identified using lowercase abbreviations. ADD, M. adductor magnus, dorsal head; ADL, M. adductor longus; ADV, M. adductor magnus, ventral head; CGI, M. coccygeoiliacus; CR, M. cruralis; GLM, M. glutaeus magnus; GMA, M. gracilis major; GMI, M. gracilis minor; GML, M. gemellus; IE, M. iliacus externus, superficial layer; IE′, M. iliacus externus, middle layer; IE″, M. iliacus externus, extra middle layer; IE′″, M. iliacus externus, deep layer; IFB, M. iliofibularis; IFM, M. iliofemoralis; II, M. iliacus internus; IL, M. iliolumbaris; LGD, M. longissimus dorsi; lp, ligamentous plate; OBE, M. obturator externus; OBI, M. obturator internus; PT, M. pectineus; PY, M. pyriformis; SA, M. sartorius; SM, M. semimembranosus; ST, M. semitendinosus; TFL, M. tensor fascia latae.
