Figure 11.
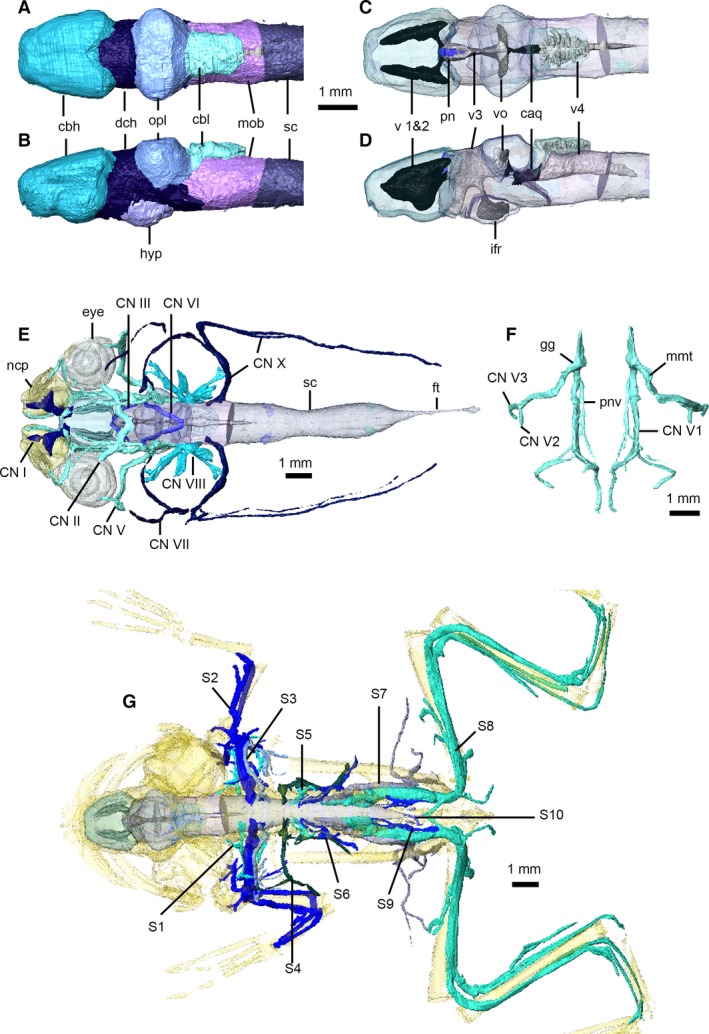
Nervous system of Xenopus laevis. Brain in dorsal (A,C) and left lateral (B,D) views, with brain transparent in (C) and (D) to illustrate internal ventricles and pineal body. Cranial nerves in dorsal view (E), with eyes, nasal capsules, brain and spinal cord transparent. Left and right trigeminal nerves (F) in dorsal view. Peripheral nervous system in dorsal view (G), with brain, spinal cord and skeleton transparent (cranial nerves not shown). caq, cerebral aqueduct; cbl, cerebellum; cbh, cerebral hemispheres; CN I–X, cranial nerves 1–10; dch, diencephalon; ft, filum terminale; gg, Gasserian ganglion; hyp, hypothalamus; ifr, infundibular recess; mmt, maxilla‐mandibular trunk; mob, medulla oblongata; ncp, nasal capsules; opl, optic lobes; pn, pineal body; pnv, palatine nerve; S 1–10, spinal nerves 1–10; sc, spinal cord; v 1 and 2, first and second ventricles; v3, third ventricle; v4, fourth ventricle; vo, optic ventricles.
