Figure 6.
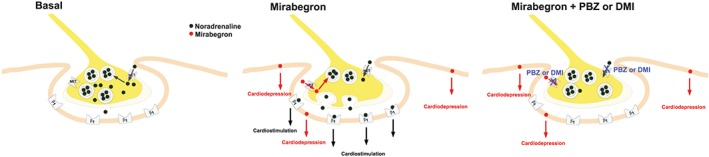
Proposed effects of mirabegron in human heart. In sympathetic nerve terminals, noradrenaline is stored in storage vesicles (Basal). Synaptic noradrenaline is a substrate for neuronal uptake in the neuron by the noradrenaline transporter (NET, neuronal uptake, Chen et al., 2004). It is proposed that mirabegron is taken up into sympathetic nerve terminals by the NET transporter, causes release of noradrenaline from storage vesicles by exocytosis which in turn activates β1‐adrenoceptors (β1) on post‐junctional membranes of the myocardial cell. Mirabegron causes cardiodepression by an unknown mechanism (see text for further discussion). Thus mirabegron simultaneously causes cardiostimulation by an indirect mechanism and cardiodepression. The cardiostimulant, but not the cardiodepressant, effects of mirabegron can be prevented by neuronal uptake blockers phenoxybenzamine (PBZ) or desipramine (DMI) or by blockade of β1‐adrenoceptors.
