Fig. 5. Attenuation of VEGFR3 contributes to the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension in humans.
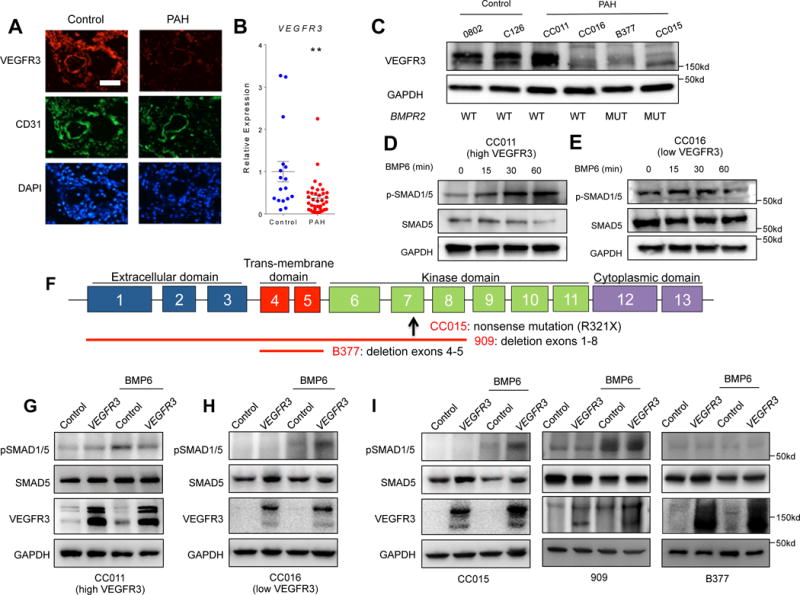
(A) Immunofluorescence staining of a normal lung section (left) and a PAH lung section (right) for endothelial cells (CD31; green), VEGFR3 (red), and nuclei (DAPI; blue) showing decreased VEGFR3 expression in PAH endothelium. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Relative expression level of VEGFR3 mRNA in normal and PAH PAECs. The significance was calculated using Wilcoxon rank-sum test. **P < 0.01 (C) Overall decreased but heterogeneous VEGFR3 protein expression among PAH patient-derived PAECs is not dependent on mutations in BMPR2. The mean of all the expression values in the control group were used for normalization. (D–E) Expression level of VEGFR3 influences the response of PAH PAECs to BMP6 (50 ng/mL) stimulation. (D) Upon BMP6 treatment, phosphorylation of SMAD1/5 was only increased in PAH PAECs with a relatively high level of VEGFR3. (E) Phosphorylation of SMAD 1/5 did not change in PAH PAECs with low VEGFR3 expression. (F) Schematic of BMPR2 genomic loci depicting the specific gene mutation/deletion in human PAECs tested. The up-arrow depicts location of the missense mutation, and the red lines depict the locations of gene deletion. (G–I) Effect of lentiviral-mediated over-expression of VEGFR3 on BMP-ligand mediated phosphorylation of SMAD 1/5. In PAH PAEC without BMPR2 mutations with high level of VEGFR3 expression, over-expression of VEGFR3 did not increased the phosphorylation of SMAD 1/5 upon BMP6 stimulation (G), whereas in PAH PAECs with low VEGFR3 expression, over-expression of VEGFR3 restored the phosphorylation of SMAD 1/5 upon BMP6 stimulation (H). (I) In PAH PAECs from subjects with BMPR2 mutations, efficacy of rescue with VEGFR3 overexpression in enhancing BMP6 response was variable depending on the underlying BMPR2 mutation.
