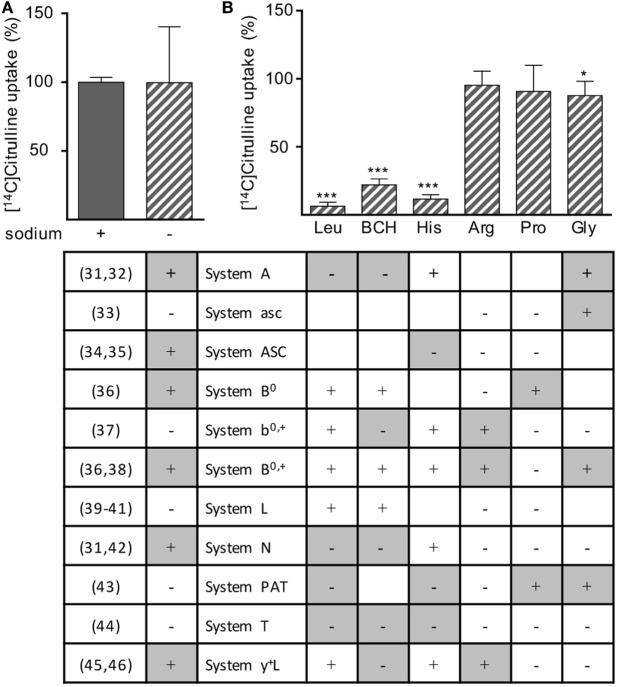
Figure 5.
Citrulline uptake into human T lymphocytes seems to be mediated by L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1). Primary human CD3+ T lymphocytes were isolated from blood of healthy donors by negative selection and stimulated for 24 h in the presence of 20 µM arginine with anti-CD3/anti-CD28-tagged particles. The uptake of 20 µM [14C]citrulline was then determined over 30 s in the presence or absence of (A) sodium or (B) in the presence of 1 mM leucine (Leu), 2-aminobicyclo-(2,2,1)-heptane-2-carboxylic acid (BCH), histidine (His), arginine (Arg), proline (Pro), or glycine (Gly). Data are expressed as percentage of the mean value obtained with the respective control cells (without any competitive amino acid and in the presence of sodium), (A) 5.0 ± 1.0 pmol citrulline/106 cells, n = 12 from 4 donors; (B) 7.4 ± 5.7 pmol citrulline/106 cells, n = 9 from three donors. Statistical calculations were performed with two-tailed t test between competitor-treated and respective control cells (***p < 0.001,*p < 0.05). The table below the respective experimental conditions denotes the expected results according to the cited published references (left column), i.e., if transported via the respective system. +: inhibition of citrulline uptake expected; −: no inhibition of citrulline uptake expected. Color coding of table: experimental results were classified as compatible (white) or not compatible (gray) with the respective transport system; empty cells: interpretation of the results equivocal.