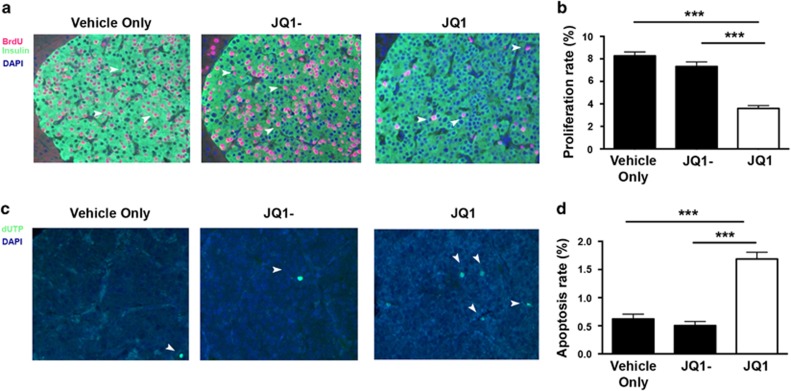
Figure 6.
Efficacy of JQ1 on proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic NETs in Men1L/L/RIP2-Cre mice. Thirty week old Men1L/L/RIP2-Cre mice (n=8; 4 males and 4 females) were injected, i.p., with JQ1 twice weekly for one month, and the pancreas removed to study PNET growth. (a) Immunohistochemistry of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation into proliferating PNET cells. BrdU stained cells are indicated in red and by the white arrows. PNETs were counterstained with DAPI (blue) to highlight the nucleus of individual cells, and insulin (shown in green) to define the tumor size. (b) Apoptosis in PNETs were detected using TUNEL assay. Apoptotic cells are indicated by the addition of labelled dUTP (green, and indicated by white arrows). All sections were counterstained with DAPI to detect individual cells and tumor areas were defined by analysis of serial sections stained for insulin. All images are at x200 magnification. (c) Only cells co-staining for BrdU and insulin were included for quantification analysis of BrdU incorporation. Proliferation rate was determined as percentage of BrdU and insulin immunostaining per tumor, with n=3 tumors counted from n=4 sections per mouse. *P<0.05 and **P<0.005. Control treatments are indicated by black bars, and JQ1 treatment by a white bar. (d) Quantification of apoptosis rates. Apoptosis rate was calculated as the percentage of dUTP positive cells per tumor, with n=3 tumors counted from n=4 sections per mouse. ***P<0.0005. Control treatments are indicated by black bars, and JQ1 treatment by a white bar. The efficacy of JQ1 in male and female mice was the same. Statistical significance was assessed using a one-way ANOVA.