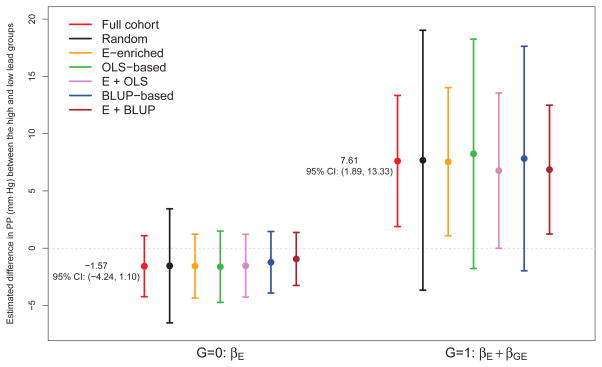
Figure 3.
NAS results: average estimated exposure effects on the pulse pressure among carriers of the H63D variant (G = 1) or subjects with wild types (G = 0), under different study designs using the FCL (n = 200, N = 706). Personal cumulative lead exposure was measured at patella bone on a continuous scale, and then dichotomized to reflect a rare exposure with a prevalence of 0.1 (High: ≥ 52μ g/g). The numbers on the graph show estimated and corresponding 95% confidence interval of exposure effects by genetic subgroups in a full cohort analysis using linear mixed model with random intercept and random slope of time.