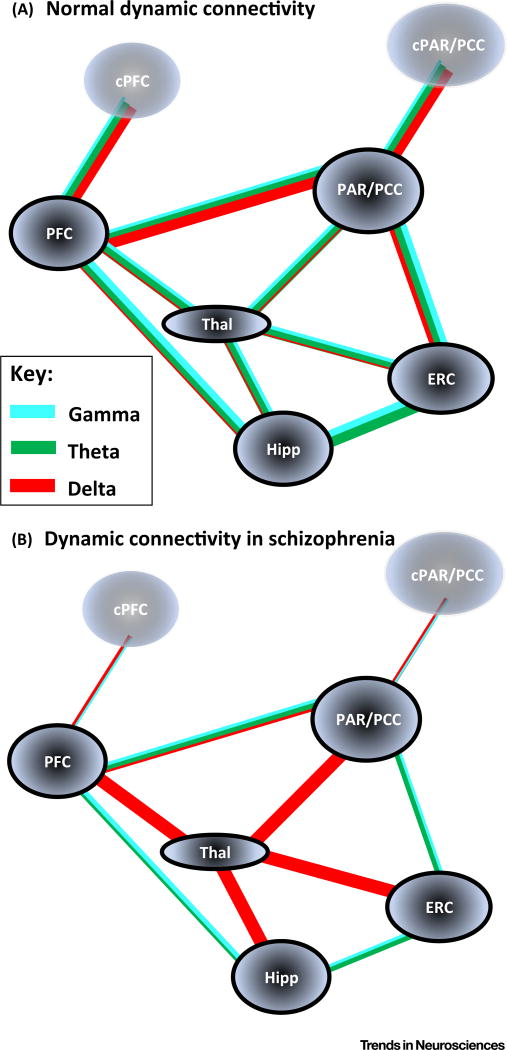
Figure 4. Frequency Mismatches in Core Default Mode Network (DMN) Regions and Related Sub- and Temporal Cortical Areas May Disrupt Internal Memory Recall/’Mental Time Travel’ Networks.
(A) Cartoon suggesting the core large-scale dynamic connectivity pathways and the relative contributions of locally generated delta (1–4 Hz, red lines), theta (5–8 Hz, green lines), and gamma (30–80 Hz, blue lines) rhythms to their functional interactions. The main neocortical regions of note form the core anterior and posterior components of the DMN (bilaterally represented), coupled predominantly with delta rhythms (see main text). In addition, the connectivity of these nodes with archi- and periallocortical areas (hippocampus and entorhinal cortex), and relevant thalamic nuclei (anterior and midline) is shown. Note the overall balance between gamma/theta-mediated interactions and the dominance of ipsilateral cortico-cortical delta-mediated interactions. (B) Cartoon summarising the precedented functional connectivity changes and local network oscillation changes in the network summarised in (A). Note the overall deficit in direct cortico-cortical interaction frequencies in favour of indirect interactions mediated by excessive thalamic delta rhythm generation. Interhemispheric interactions are shown losing their faster frequency components in line with the deficits in NR2A receptors in schizophrenia, the higher temporal precision and selective role of this subunit in inter- versus intrahemispheric connectivity [28], and the observation of interhemispheric delta phase-modulated coupling during hallucinations [85]. Reported changes in primary sensory and attentional network are not illustrated here for clarity and brevity. Abbreviations: ERC, entorhinal cortex; Hipp, hippocampus; PFC, prefrontal cortex (cPFC, contralateral); Par/PCC, parietal cortex/posterior cingulate cortex (cPAR/PCC, contralateral); Thal, thalamus.