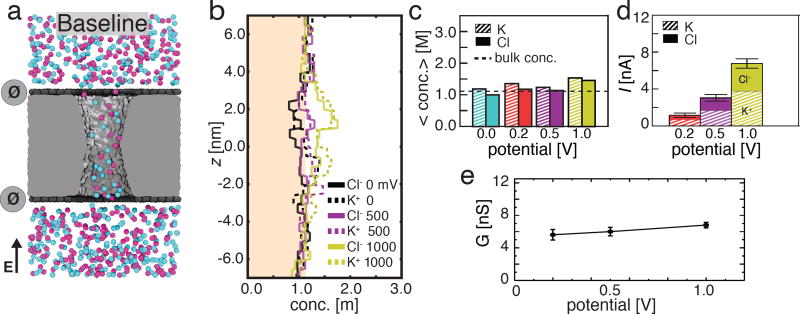
Figure 2.
Ionic conductivity of uncharged (baseline) graphene nanopore capacitor. (a) Representative configuration of ions in an uncharged nanopore capacitor. The nanopore capacitor is shown in a cut-away representation, purple and light blue spheres represent Cl− and K+ ions, respectively. The top and bottom graphene layers are electrically neutral (σtop = σbottom = 0 e nm−2), which is schematically indicated by the dark grey circles. The particular molecular configuration shown corresponds to a transmembrane bias of 200 mV. (b) The average concentration of Cl− (solid) and K+ (dashed) ions along the pore axis at 0 mV (black), 500 mV (purple), and 1 V (yellow) transmembrane bias (the profiles at 200 mV are omitted for clarity). The shaded region indicates concentrations below the bulk concentration of 1.1 M. The concentration profiles were obtained by averaging over 0.5 nm-radius disks centered at the pore axis and over the last 15 ns of the respective 25 ns MD trajectory. (c) The total average concentration of K+ (striped) and Cl− (solid) ions inside the nanopore at transmembrane biases of 0 mV (blue), 200 mV (red), 500 mV (purple), and 1000 mV (yellow). The average concentrations were obtained by averaging the concentration profiles from panel b within the region of |z| < 2.0 nm where z =0 nm is at the center of the nanopore. (d) The average ionic current (total height of each bar) and the currents carried by K+ (striped) and Cl− (solid) species at 200 mV (red), 500 mV (purple), and 1 V (yellow) transmembrane bias. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean value. (e) The simulated conductance of the uncharged nanopore capacitor versus the transmembrane bias.