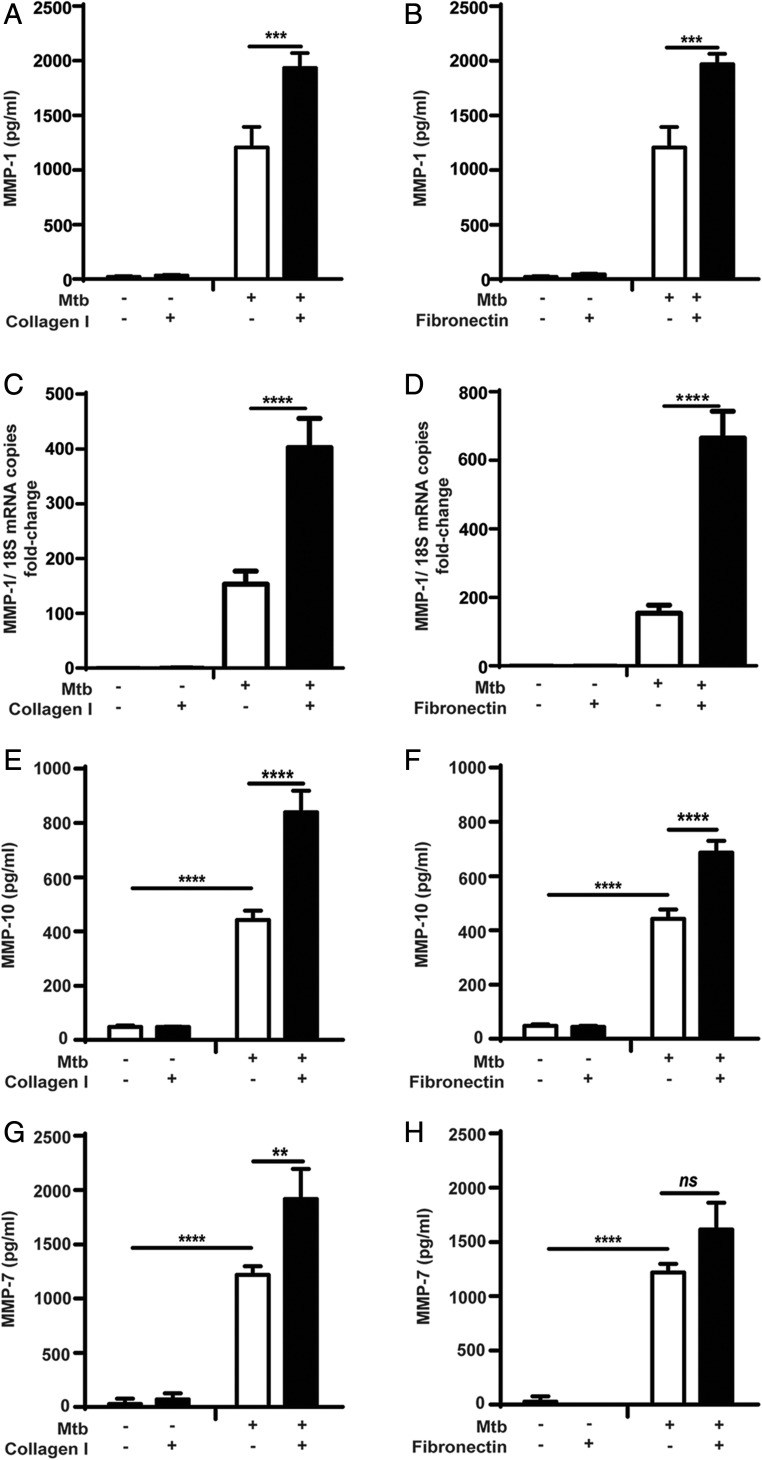
FIGURE 1.
Secretion of MMP-1, -10, and -7 by M. tuberculosis–infected primary monocytes is increased by adhesion to type I collagen and fibronectin. Monocytes in the presence or absence of type I collagen, or fibronectin were infected with M. tuberculosis (MOI = 1). For secretion analysis, supernatants were collected at 24 h poststimulation, whereas for gene expression cell lysates were collected at 6 h. MMP-1 concentrations were upregulated in M. tuberculosis–infected monocytes adherent to (A) type I collagen; (B) fibronectin, and MMP-1 mRNA accumulation was also upregulated in the presence of (C) type I collagen and (D) fibronectin. Samples were normalized to 18S rRNA. Secretion of (E and F) MMP-10, and (G and H) MMP-7 was also upregulated in the presence of type I collagen and fibronectin, after 24 h of M. tuberculosis infection. Graphs show means ± SD and are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.001. ns, not significant.