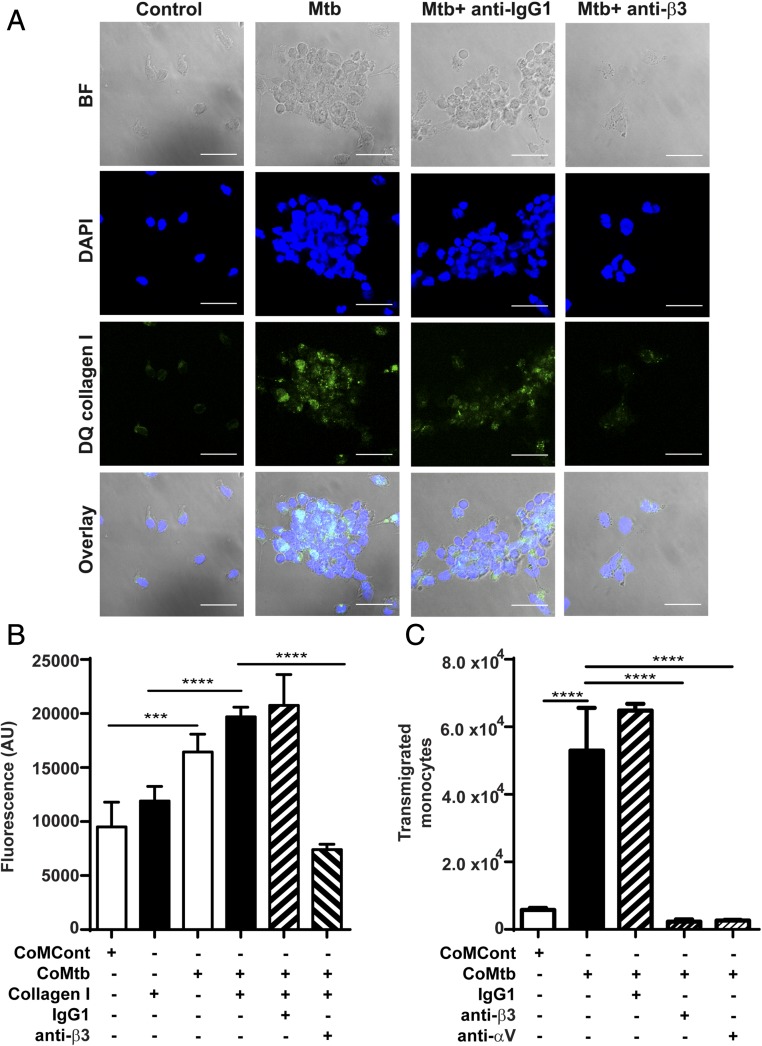
FIGURE 7.
Integrin αVβ3 upregulates type I collagen breakdown and increased monocyte adhesion and transmigration in M. tuberculosis infection. Slides were precoated with DQ type I collagen in which FITC is quenched and fluorescence is released only in areas of collagen degradation. Monocytes were preincubated with or without a function blocking anti-integrin β3 Ab or anti-IgG1 isotype control, followed by M. tuberculosis infection (MOI = 1). (A) Panels show brightfield, DAPI nuclear counterstain (blue), collagen degradation (green), and merged images. Scale bar, 25 μm. (B) CoMtb stimulation increased monocyte adhesion compared with CoMCont, which was blocked by inhibition of integrin β3. Next 1 × 105 monocytes per well were prestained with CellTracker Green CMFDA dye were stimulated with CoMtb or CoMCont. Integrin β3–mediated adhesion was inhibited with anti-integrin β3 Ab. Control monocytes preincubated with IgG1 isotype Abs. (C) Monocyte migration is increased with CoMtb stimulation, which is blocked with inhibition of integrin αV or β3. Transwells were precoated with type I collagen, and CoMtb or CoMCont was added to the basal side in a 1:2 dilution. Integrins were blocked with anti-integrin αV and β3 Abs, or an IgG1 isotype control Ab. Bars show mean ± SD. Data are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.