Figure 2.
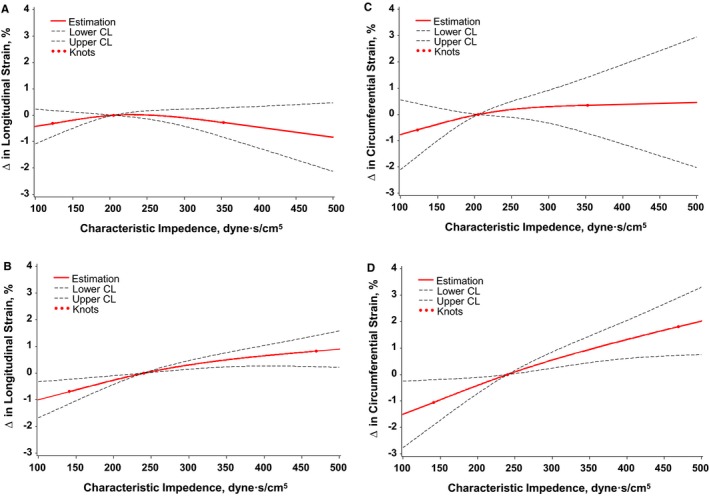
Multivariable adjusted associations between characteristic impedance (Zc) and global longitudinal strain (GLS) in (A) men and (B) women and between Zc and global circumferential strain (GCS) in (C) men and (D) women. Greater Zc was not significantly associated with either GLS or GCS in men; by contrast, Zc was associated with significantly worse (less negative) GLS and GCS. Analyses were adjusted for key covariates: cohort, age, sex, height, weight, glucose, total/HDL cholesterol ratio, natural log‐triglycerides, diabetes mellitus, current smoker, antihypertensive medication use, lipid‐lowering medication use, heart rate, systolic blood pressure, augmentation index, left ventricular mass, left ventricular wall thickness, and left ventricular diastolic dimension. The symbol Δ refers to difference in GLS or GCS compared to the median per Zc value. CL indicates confidence limit; HDL, high‐density lipoprotein.
