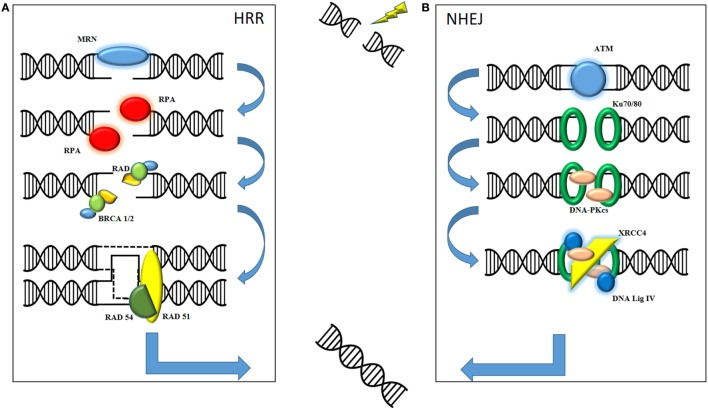
Figure 1.
Ionizing radiation causes fatal double-strand breaks. DNA damage repair is mediated by two main pathways: homologous recombination repair (HRR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). (A) In HRR, damage is sensed by the MRE11–Rad50–Nbs1 (MRN) complex, consisting of MRE11, Rad50, and Nbs1, which facilitates recruitment of downstream mediators to the site of damage. These include replication protein A (RPA), the Rad family of proteins and BRCA1 and BRCA2. Final sequence homology for the damaged DNA is provided by invading, and requires the presence of, the sister chromatid. (B) NHEJ is initiated by the recruitment of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-related kinase (PIKK) family such as ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM). These facilitate the recognition of damaged strands by Ku70/Ku80, subsequent processing by DNA-PKcs and final repair and processing of strand ends by XRCC4 and DNA Ligase IV. The final product of both pathways is a repaired, complete strand of DNA.