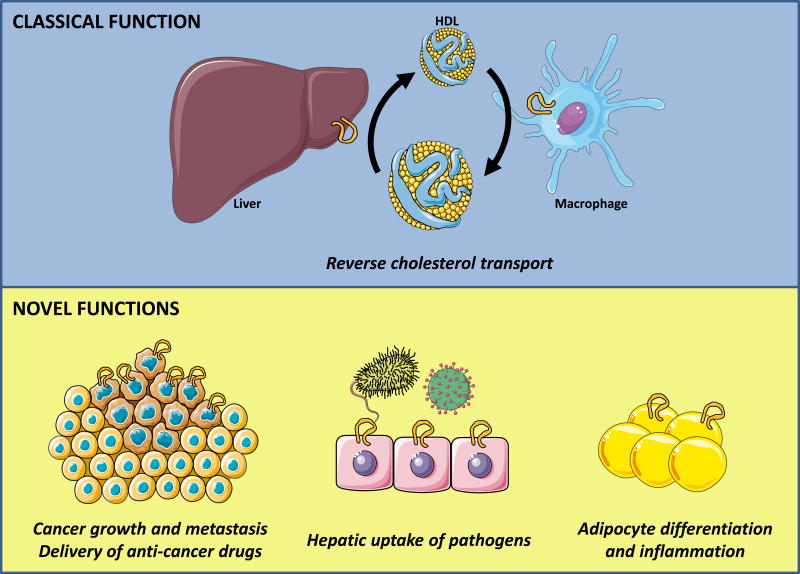
Figure 1. Classical and novel functions of SR-BI in physiology and disease.
Top, shows classical function of liver SR-BI which is responsible for the uptake of HDL-cholesterol for elimination into bile; macrophage SR-BI can transport cholesterol bi-directionally but is believed to unload or efflux excess peripheral cholesterol to HDL which can then go to the liver for completion of reverse cholesterol transport. Bottom, shows newly described novel functions of SR-BI in cancer growth and metastasis, hepatic uptake of pathogens and adipocyte differentiation and inflammation. High SR-BI expression in tumors potentially increases the ability to metastasize, but also provides an opportunity to selectively deliver anti-cancer drugs through packaging in recombinant HDL particles (bottom left). Hepatic SR-BI mediates the uptake of bacteria as well as viruses thereby contributing to the host response to infection (bottom middle). SR-BI fluxes cholesterol from and into adipocytes and thereby modulates the inflammatory state of adipose tissue (bottom right).