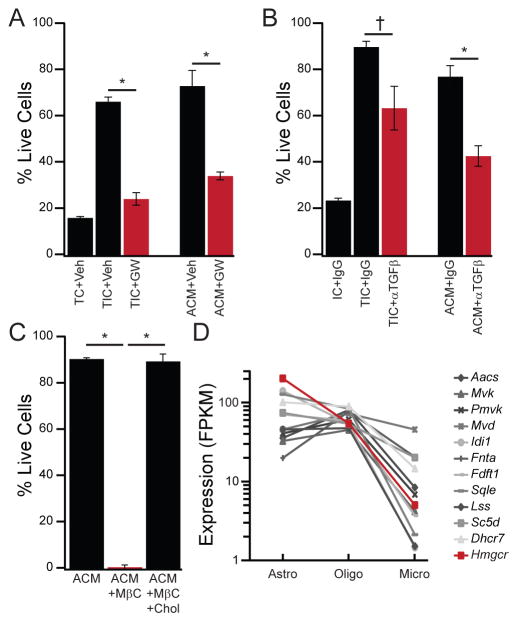
Figure 3. CSF-1/IL-34, TGF-β, and cholesterol are necessary for ACM survival activity.
(A) The CSF1R antagonist GW2580 (10 μM, red), but not vehicle (Veh, black), reduced survival of primary rat microglia in both TIC and ACM. (B) The pan-TGF-β neutralizing antibody 1D11 (5 μg/mL), but not IgG control, partially reversed survival in TIC or ACM (20 μg/mL). (C) The cholesterol-chelating agent methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβC, 5 mM) eliminated ACM survival activity, but not if it was pre-saturated with cholesterol (MβC+ chol). (D) Abundance of cholesterol biosynthesis machinery mRNA transcripts from published RNA-seq datasets (Zhang et al., 2014) expressed as fragments per kilobase per million reads mapped (FPKM) illustrates lower levels in microglia (Micro) as compared to astrocytes (Astro) and mature oligodendrocytes (Oligo). The rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis (Hmgcr) is highlighted in red. Averages are mean ± sem. * P < 0.005, † P < 0.05 Student’s t-test.