Figure 4.
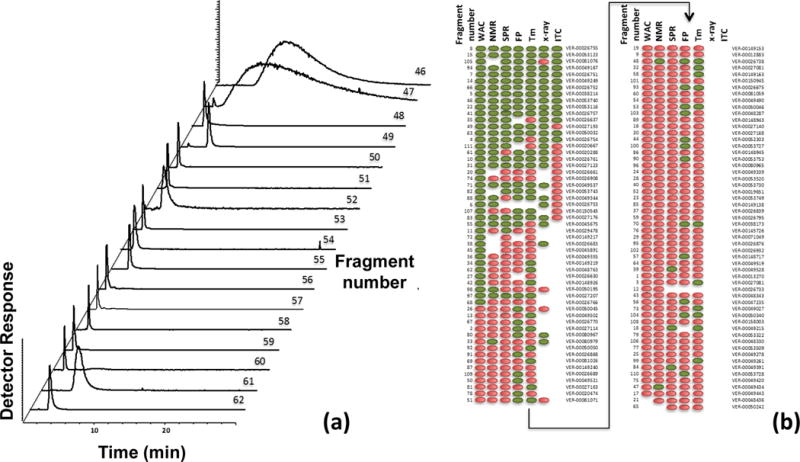
Use of weak affinity chromatography (WAC) to screen the binding of drug fragments, as illustrated by employing a column containing the immobilized ATPase domain of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90). A), chromatograms obtained for fragments 46–62, out of a total of 111 drug fragments tested. B), results obtained for all 111 drug fragments when screened for their binding to HSP90 by using WAC, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, surface plasmon resonance (SPR) spectroscopy, a fluorescence polarization (FP) assay, or a thermal shift assay (Tm), with some results also being included based on X-ray crystallography and isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). The hits for binding are indicated by green (or dark gray) and non-hits are represented by red (or light gray). Adapted from Ref. (42) with permission from the American Chemical Society.
