Figure 3. NMR characterization of RNF169 in complex with H2A-H2B and the nucleosome ubiquitylated at H2AK15.
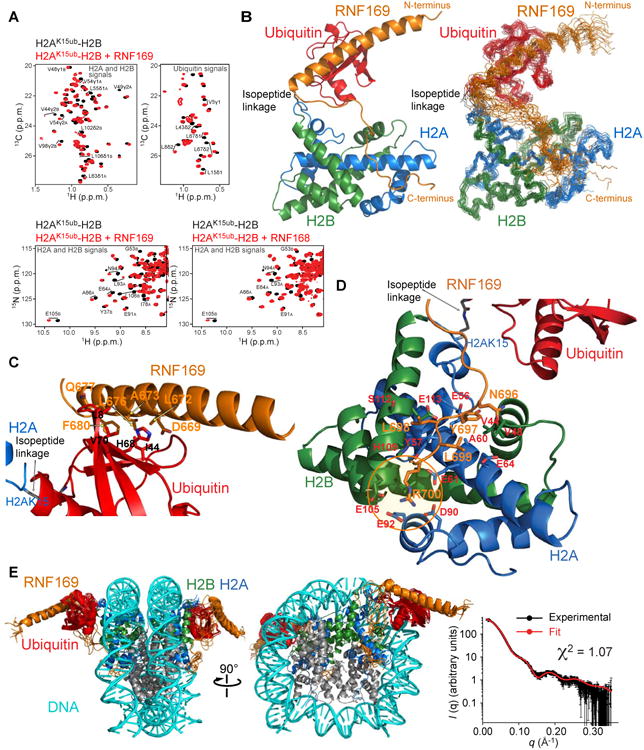
(A) Top: Regions of methyl-TROSY spectra of H2AK15ub-H2B selectively 1H-13C-labeled at methyl groups of Ile, Leu and Val residues of H2A-H2B or ubiquitin in an otherwise perdeuterated background, free (black) and bound to unlabeled RNF169 (red). Bottom: Regions of 1H-15N TROSY HSQC spectra of H2AK15ub-H2B prepared with 15N-labeled H2A-H2B and unlabeled ubiquitin, free (black) and bound to unlabeled RNF169 or RNF168 (red). Suffix A is for H2A and B for H2B.
(B) Cartoon representation and NMR structure ensemble of H2AK15ub-H2B in complex with RNF169.
(C) Cartoon representation of a region of the H2AK15ub-H2B–RNF169 complex highlighting the interaction of RNF169 α-helix and ubiquitin. Key residues are in stick representation.
(D) Cartoon representation of a region of the H2AK15ub-H2B–RNF169 complex highlighting the interaction of RNF169 LRM with H2A-H2B. Key residues are in stick representation. H2A-H2B acidic patch area binding RNF169 Arg700 is circled in orange.
(E) NMR/SAXS-based model of NCPH2AK15ub in complex with RNF169. Goodness of fit of the model to SAXS data recorded for the NCPH2AK15ub–RNF169 complex.
