Figure 6. Effects of RNF168, RNF169 and RAD18 on the association of 53BP1 with the nucleosome ubiquitylated at H2AK15 and dimethylated at H4K20.
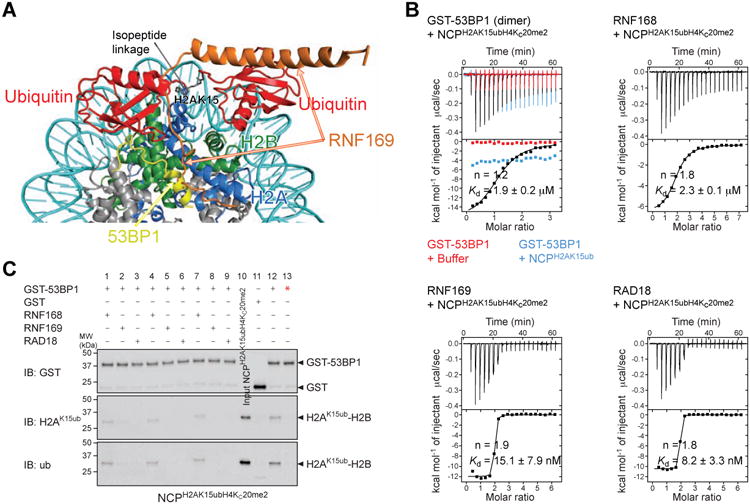
(A) Overlay of the cryo-EM structure of NCPH2AK15ubH4Kc20me2–53BP1 (aa 1611-1631) and NMR/SAXS-based model of NCPH2AK15ub–RNF169 (aa 653-708).
(B) ITC results for the interactions of GST-53BP1 (aa 1484-1635) dimer, RNF168, RNF169 and RAD18 with NCPH2AK15ubH4Kc20me2. The GST-53BP1–NCPH2AK15ub interaction was also probed. n is the stoichiometry of binding. Kds are reported with s.d. determined by nonlinear least-squares analysis.
(C) GST pull-down assays of NCPH2AK15ubH4Kc20me2 in the absence (lane 12) and presence of equimolar (lanes 1-3), 2-fold (lanes 4-6) and 4-fold (lanes 7-9) molar excess of RNF168, RNF169 and RAD18 with GST-53BP1 (aa 1484-1635), immunoblotted (IB) for GST, K15-ubiquitylated H2A (H2AK15ub) and ubiquitin (ub). Pull-downs of NCPH2AK15ubH4Kc20me2 with GST (lane 11) and GST-53BP1 (aa 1484-1635) T1609E/S1618E mutant (lane 13, red star) were done as negative controls. 53BP1 T1609E/S1618E is unable to bind NCPH2AK15ubH4Kc20me2 as reported (Lee et al., 2014; Orthwein et al., 2014). Input NCPH2AK15ubH4Kc20me2 is in lane 10.
