Figure 4.
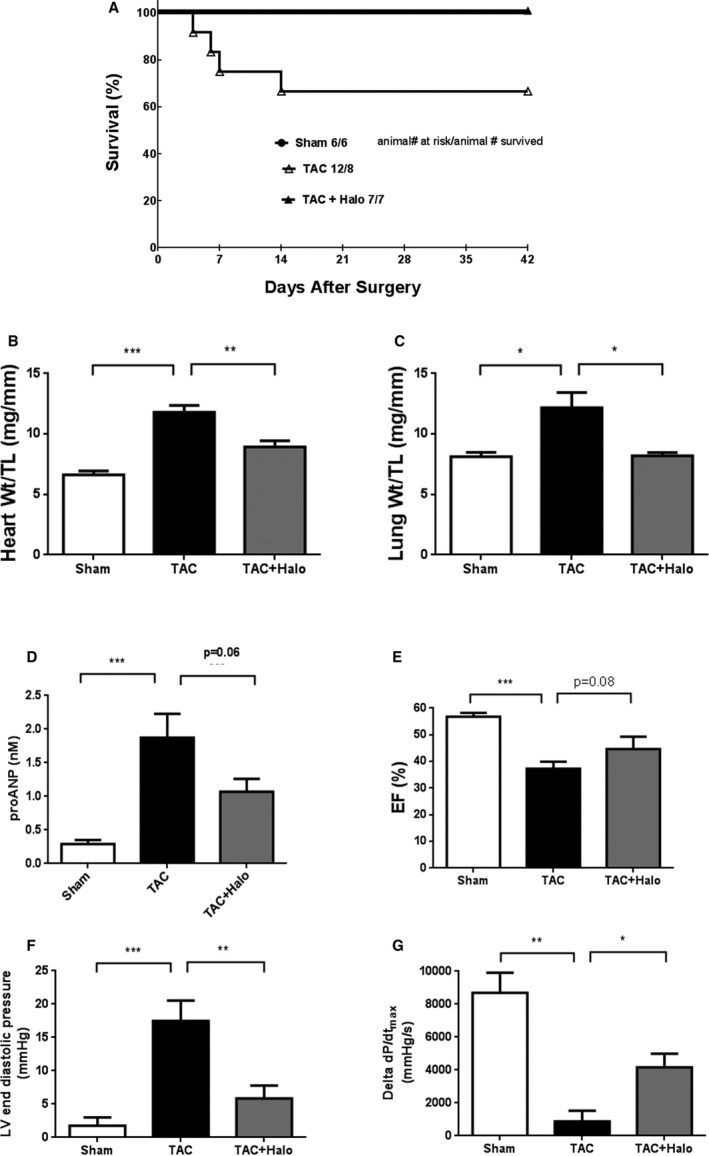
Halofuginone in TAC (transverse aortic constriction) mouse model. Male C57Bl/6J mice were subjected to TAC to induce heart failure. Halofuginone was delivered in chow (0.3 mg/kg dose) starting on the same day that TAC was performed. Survival was monitored in each group. A, Log rank survival test, TAC vs TAC+Halo, P=0.1. At end of study (6 weeks), heart weight, lung weight, and tibia length were recorded, and ratios were calculated (B and C). Circulating proANP (pro–atrial natriuretic peptide) level was measure by ELISA (enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay, [D]). Ejection fraction (EF) was measured by echocardiography at the end of study (E). Left ventricle end‐diastolic pressure at baseline and the change in cardiac contractility (ΔdP/dT) following dobutamine challenge were measured at the end of study (F and G). There were 6 (6), 12 (8) and 7 (7) mice in the sham, TAC, and TAC+halofuginone groups at the beginning of the study, respectively. Numbers in the parentheses reflect the number of animals that survived until the end of the study, which were used for analysis (B through G). Unpaired t test was used for statistics: *, **, ***, P<0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively.
