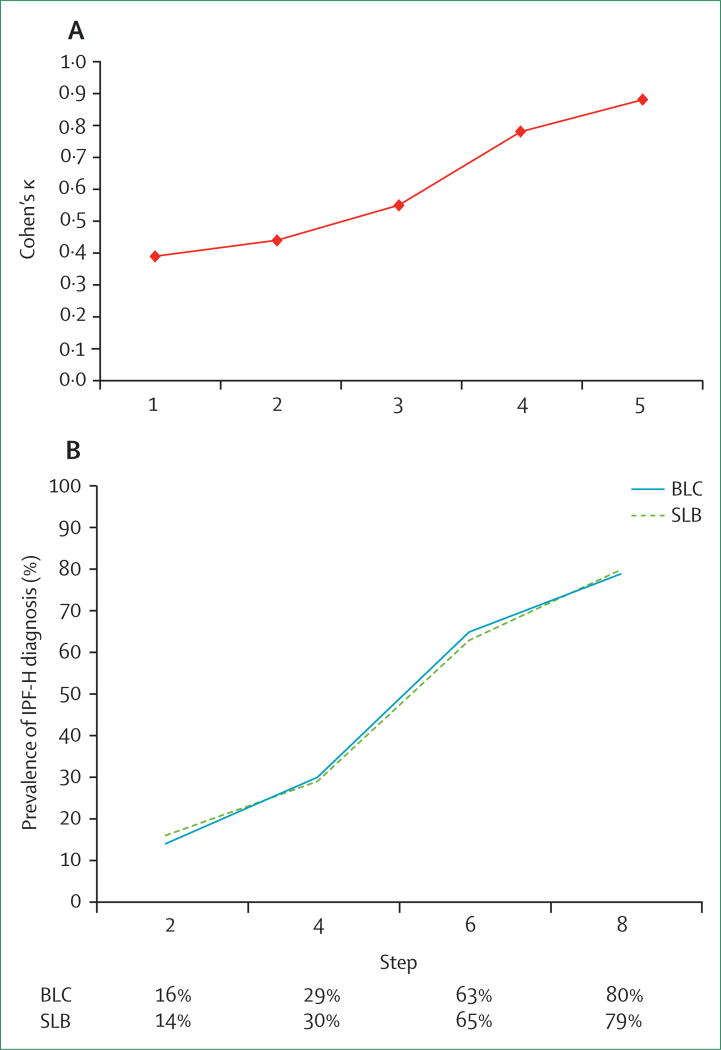
Figure 2. Effect of multidisciplinary diagnostic approach on diagnosis in interstitial pneumonias.
(A) Interobserver agreement among clinicians and radiologists in the evaluation of patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Step 1: individual assessment of high-resolution CT data alone. Step 2: individual assessment of high-resolution CT plus clinical data. Step 3: group discussion of high-resolution CT plus clinical data. Step 4: group discussion of high-resolution CT, clinical, and surgical lung biopsy data. Step 5: consensus diagnosis among all participants. Adapted from Flaherty and colleagues.68 (B)The effect of bronchial cryobiopsy and surgical lung biopsy on diagnostic confidence in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis during multidisciplinary team evaluation. Step 2: addition of clinical and radiological data. Step 4: addition of bronchoalveolar lavage data. Step 6: addition of biopsy data. Step 8: addition of follow-up data. Reproduced with permission from Tomassetti and colleagues.69 BLC=bronchial cryobiopsy. IPF-H=idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis diagnosis made with high confidence. SLB=surgical lung biopsy.