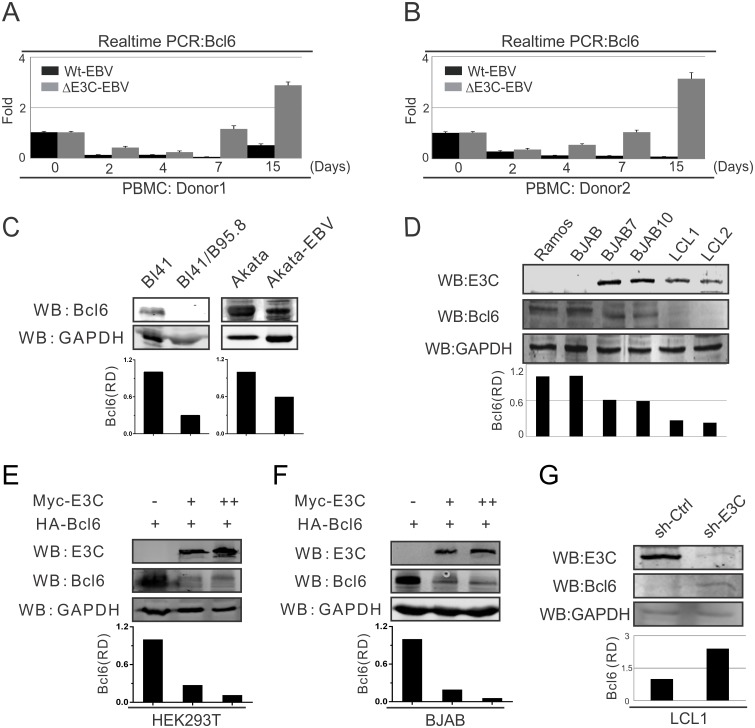
Fig 1. EBNA3C down-regulates Bcl6 expression in EBV-infected PBMCs.
A-B) 10 million human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from donor 1 and donor 2 were infected with BAC-GFP wild-type EBV or ΔE3C-EBV for 4 hours. Cells were harvested at indicated time points, then total RNA was isolated and subjected to cDNA preparation according to the manufacture's instruction followed by quantitative Real-time PCR for detecting Bcl6 transcription levels. C) 10 million Burkitt’s lymphoma (BL) cells BL41 or Akata and EBV-positive BL41/B95.8 or Akata-EBV cells were lysed with RIPA buffer and western blot analysis was performed with indicated antibodies. The relative density (RD) of Bcl6 protein was quantified and shown. D) 10 million EBV-negative Ramos, BJAB; EBNA3C stably expressed BJAB7, BJAB10; EBV-transformed LCL1, LCL2 cells were harvested and total cell lysates were subjected to western blot analysis using indicated antibodies. E-F) 10 million E) HEK293T and F) Saos-2 cells were transfected in a dose-dependent manner with increasing amounts EBNA3C constructs and western blot analysis was performed using specific antibodies as indicated. G) Lentivirus mediated stable EBNA3C knock-down (sh-E3C) or scramble control (sh-Ctrl) LCL1 cells were subjected to western blot analysis with indicated antibodies. Protein bands from western blot were analyzed by the Odyssey imager software and represented as bar diagrams based on internal loading control GAPDH. These results shown are representative of three independent experiments.