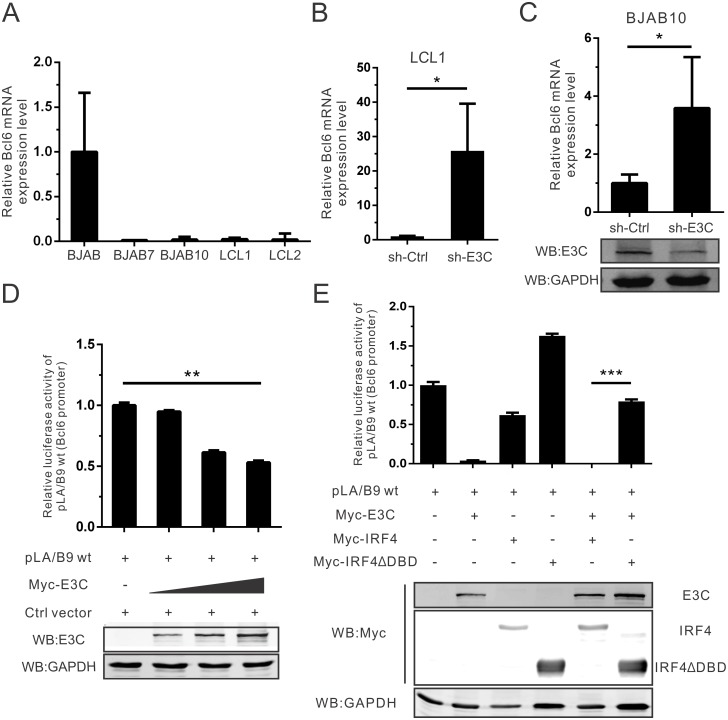
Fig 5. EBNA3C regulates Bcl6 mRNA expression through inhibition of its promoter activity.
A) 5 million BJAB, BJAB7, BJAB10, LCL1 and LCL2 cells were harvested and extracted total RNA using Trizol reagent. Then cDNA was prepared with reverse transcriptase kit, and detected Bcl6 mRNA expression by quantitative Real-time PCR analysis (SYBR green). GAPDH was set as an internal reference. Each sample was determined in triplicate. B) EBNA3C knock-down (sh-E3C) stable LCL1 or control (sh-Ctrl) LCL1 cells were harvested and Bcl6 mRNA expression was detected using Real-time PCR as mentioned. C) 10 million BJAB10 cells were transfected with specific EBNA3C (sh-E3C) or control (sh-Ctrl) short hairpin RNA. At 48 hours post-transfection, total RNA was extracted, reverse-transcribed, followed by quantitative Real-time PCR analysis. Meanwhile, EBNA3C expression was also detected by western blot analysis. D) HEK293T cells were transfected with the reporter constructs containing wild-type Bcl6 promoter (pLA/B9) and increasing amount of Myc-EBNA3C. Cells were collected and lysed in lysis buffer at 48 hours post-transfection. Luciferase activity was measured according to the dual-luciferase reporter assay kit. Mean values and standard deviations of two independent experiments were presented. Cell lysate was resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE in order to check EBNA3C expression. GAPDH western blot was done as an internal loading control. E) HEK293T cells were transfected with wild-type Bcl6 promoter reporter plasmids in combination with different expression constructs as indicated. Cells were collected and lysed, then the lysate were used to detect luciferase activity as previously described.