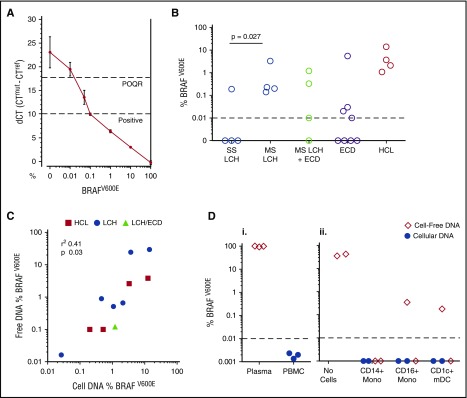
Figure 2.
Detection of BRAFV600E alleles. (A) A standard curve constructed using DNA purified from a dilution series of BRAFV600E-positive melanoma cell line A375 into WT Epstein-Barr virus–transformed lymphoblastoid cell line. The quantitative limit of detection was 0.1%; the absolute limit of detection was 0.01% (positive outside of quantitative range [POQR]). (B) BRAFV600E allele frequency in bulk PBMCs in cases of lesion BRAFV600E + LCH, LCH/ECD, and ECD. Contingency of positive PBMCs upon MS-LCH tested by Fisher’s exact test. (C) Correlation between mutated allele burden in cell-free plasma and PBMC DNA in LCH, ECD, and HCL. (Di) Test of exogenous free DNA uptake by PBMCs. BRAF-mutated DNA (derived from melanoma cell line A375) was spiked into whole blood for 24 hours at room temperature. Plasma and PBMCs were isolated by density centrifugation. DNA was extracted from both fractions and subjected to allele-specific PCR. (Dii) Test of exogenous free DNA uptake by sorted cells incubated at 37°C for 24 hours in medium supplemented with 20% human serum from a patient with HCL. DNA from supernatants and cell pellets, as indicated, was subjected to allele-specific PCR. mDC, myeloid dendritic cell.