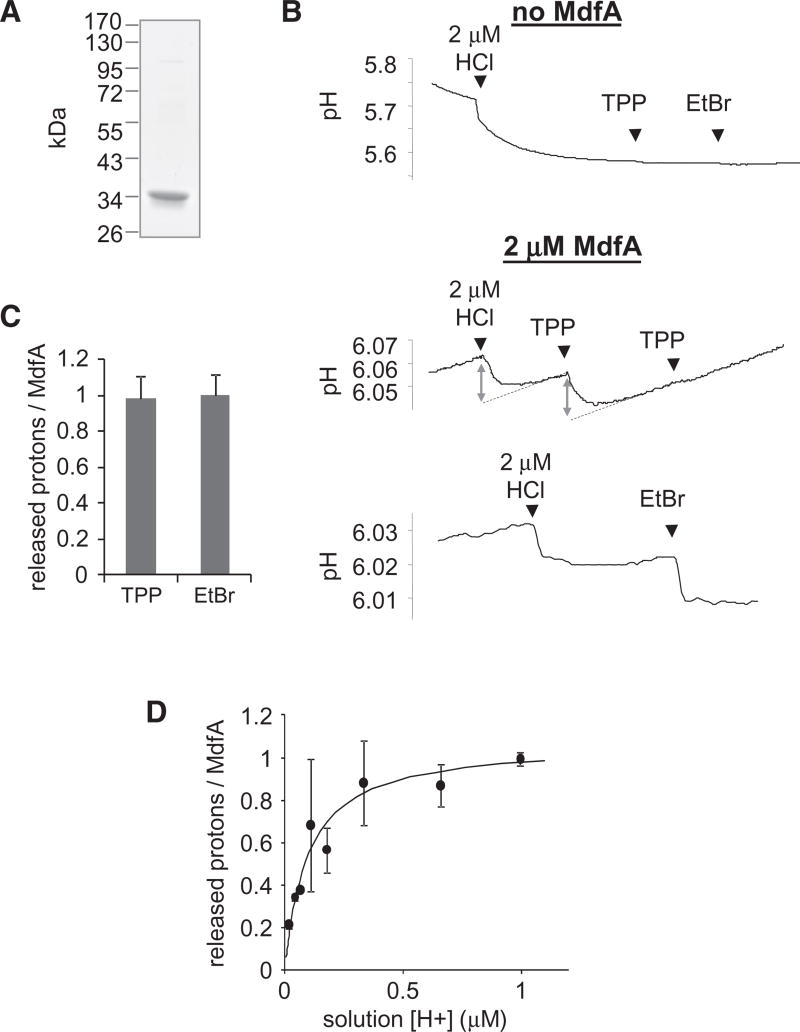
Figure 2. Substrate-Induced Proton Release.
(A) Purity of MdfA as judged by SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie.
(B) Time-dependent pH measurements; effect of adding 2 µM HCl or saturating amounts of substrates on the pH of an unbuffered solution with or without 2 µM MdfA. EtBr = ethidium bromide. To quantify the amount of proton released, the magnitude of pH changes elicited by substrate was compared with the effect of HCl (double arrows). Linear regression was utilized to compensate for pH drifts (dotted lines).
(C) Stoichiometry of protons released from MdfA upon binding TPP or EtBr. Error bars indicate SD from 15 (TPP) or 7 (EtBr) independent measurements.
(D) Effect of [H+] on the amount of protons released from MdfA upon addition of 0.3 mM TPP. The line represents a nonlinear regression fit to an equation describing saturable proton binding. The experiment was repeated three times and the error bars represent SD. See also Figure S2.