Figure 2.
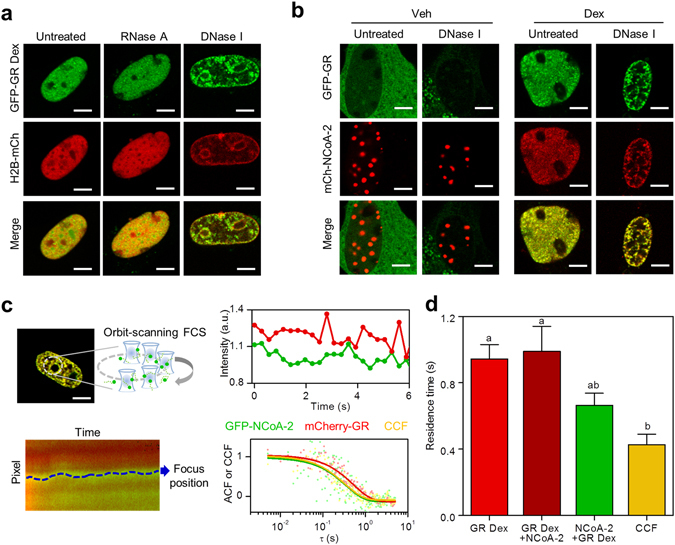
GR and NCoA-2 dynamically partition between the nucleoplasm and DNA-dependent discrete foci. Properties of GR nuclear foci in BHK cells were analyzed using biochemical and FCS-based approaches. (a) Cells co-expressing GFP-GR and H2B-mCherry were fixed, permeabilized and digested with RNase A or DNase I (Scale bar: 5 µm). (b) In situ-DNase I digestion of cells co-expressing GFP-GR and mCherry-NCoA-2 before and after stimulation with Dex (Scale bar: 5 µm). (c,d) Orbit-scanning FCS experiments were run in cells expressing either GFP-GR or GFP-NCoA-2 and mCherry-GR. (c) The laser orbits were set to scan through foci which position were further determined with subpixel precision. The intensity traces of foci were then used to calculate the autocorrelation or cross-correlation functions (representative curves). ACF data was fitted with a model that considers binding to fixed targets (continuous lines). (d) Mean residence time of mCherry-GR (dark red), GFP-NCoA-2 (green) and CCF (yellow) at foci (n = 12). Red bar corresponds to the residence time of GFP-GR in cells that were not cotransfected with NCoA-2. Bars with the same superscript letters represent data not significantly different from each other (p < 0.05).
