Figure 1.
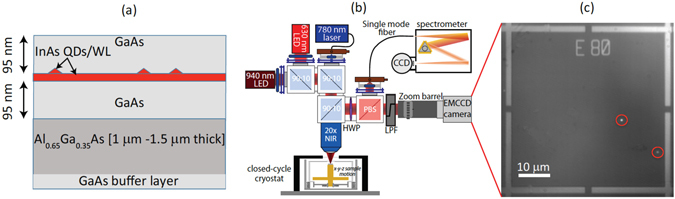
Sample structure and experimental set up (a) Schematic of the sample under study (not to scale), comprising a single layer of InAs quantum dots (red triangles), grown on an InAs wetting layer (WL) between two 95 nm thick layers of GaAs, and situated on top of a 1 μm or 1.5 μm thick Al0.65Ga0.35As layer on a GaAs buffer layer followed by a GaAs substrate. (b) Schematic of the photoluminescence setup. An infrared light emitting diode (LED, emission centered at 940 nm) is used for illumination of the sample while either a 630 nm red LED or a 780 nm laser is used for excitation of the quantum dots (QDs), depending on whether excitation over a broad area (LED) or of individual QDs (laser) is required. Samples are placed within a cryostat on an x-y-z positioner. Imaging is done by directing the emitted and reflected light into an Electron Multiplied CCD (EMCCD) camera, while spectroscopy is performed by collecting emission into a single-mode fiber and sending it to a grating spectrometer. (c) EMCCD image of the photoluminescence from two QDs (highlighted by red circles) and reflected light by the alignment marks (metallic crosses), acquired by illuminating the sample simultaneously with both the red and near-infrared LEDs, at a temperature of 4 K.
