Figure 5.
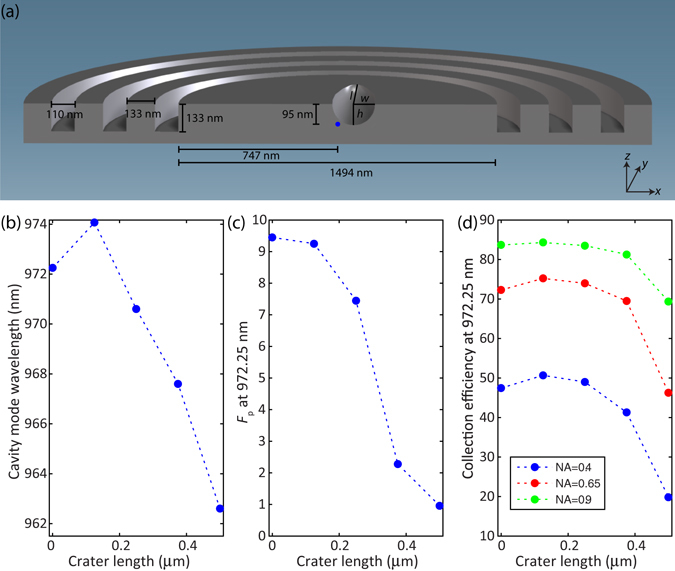
Finite-Difference Time-Domain simulations of the optical properties of a circular grating cavity containing a quantum dot and a crater-like feature close to its center. (a): Geometry of the simulated sample: the quantum dot (blue sphere) is positioned in the center of the circular grating structure. The center position of the half-ellipsoidal crater, used to depict a surface morphological (crater-like) feature, is fixed at a position x = 75 nm, y = 0 nm, z = 95 nm with respect to the QD. The crater width w is kept fixed at 125 nm, while the crater length l and crater height h have a fixed aspect ratio of 5:1, with the length l varying between 125 nm and 500 nm. The leftmost point (crater length = 0) corresponds to the circular grating structure in absence of a crater. Finite-difference time-domain simulations of the circular grating cavity wavelength (panel (b)), the Purcell factor F p (panel (c)) and collection efficiency of the QD emission into objectives with different numerical aperture (NA) (panel (d)), plotted as a function of crater length.
