FIGURE 2.
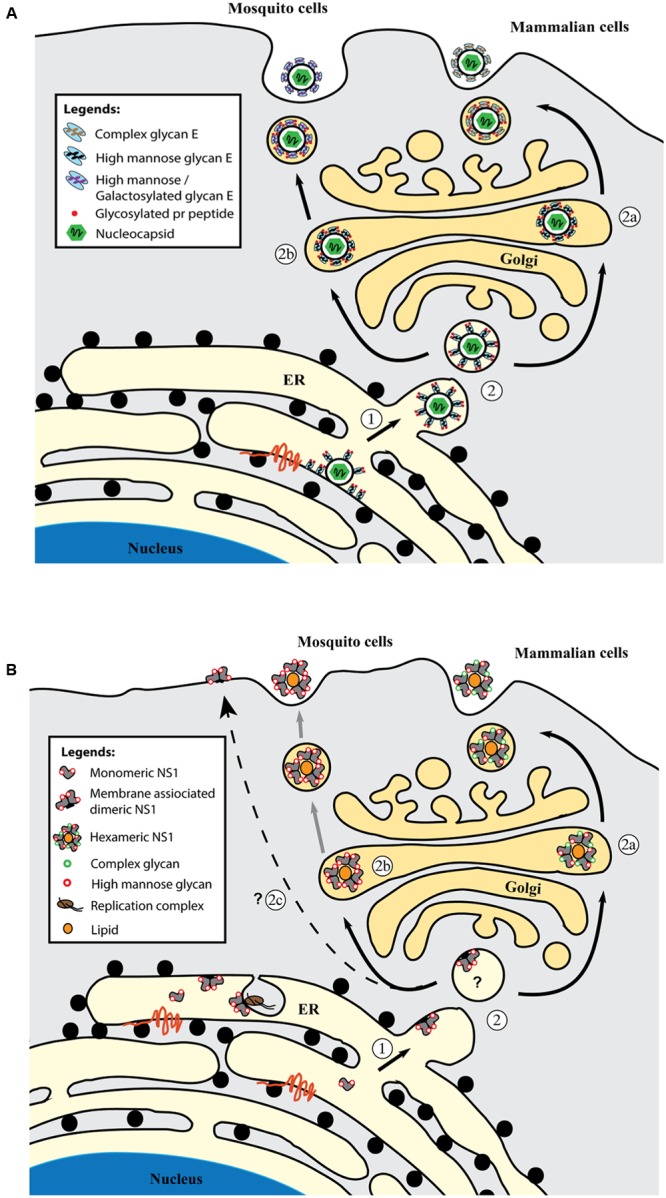
Glycosylation of DENV E (A) and NS1 (B) proteins in mammalian cells and mosquito cells. (A) In ER, newly synthesized E protein is glycosylated and heterodimerizes with prM protein to form a higher order oligomeric preassembly complex. The immature virus particle with prM-E spikes is formed when the nucleocapsid associates with prM-E-rich membranes which buds into the ER lumen (1). The glycans remain of high mannose type on the immature virus particle as it is translocated to Golgi apparatus along the secretory pathway (2). The conformational rearrangement of prM-E spikes and cleavage of prM by host protease furin occurs in the Golgi to produce a mature, smooth virus particle. In mammalian cells, the glycans are further processed and modified into complex glycans before the virus particle is released to the extracellular milieu (route 2a). In mosquito cells, majority of the glycans are high mannose or galactosylated due to the different glycosylation enzymes expressed in insect cells (route 2b). High mannose glycan on the E protein, particularly the N67-glycan facilitates DC-SIGN(+) cell infection and virus propagation. The function of complex glycan on E protein is currently unknown. The glycosylated pr peptides are bound to E protein after furin cleavage and only dissociate at neutral pH in the extracellular milieu. (B) Monomeric NS1 protein is glycosylated with high mannose glycans at N130 and N207. The monomer rapidly dimerizes in the ER and membrane-associated NS1 dimers (1) are involved in virus RNA replication. Three NS1 dimers form a soluble hexameric NS1 but the exact location of hexamer formation remains unknown (2). In mammalian cells, the N130 glycans are modified into complex glycans before the soluble NS1 hexamer is secreted out of the cells (route 2a). In mosquito cells, generation of complex glycans doesn’t happen and the lack of complex glycans (N130) on NS1 hexamer affects hexamer stability and greatly reduces its secretion (route 2b). A subset of dimeric NS1 are found on the infected cell surface but the trafficking pathway has yet to be determined (route 2c). High-mannose glycan at N207 stabilizes NS1 dimer.
