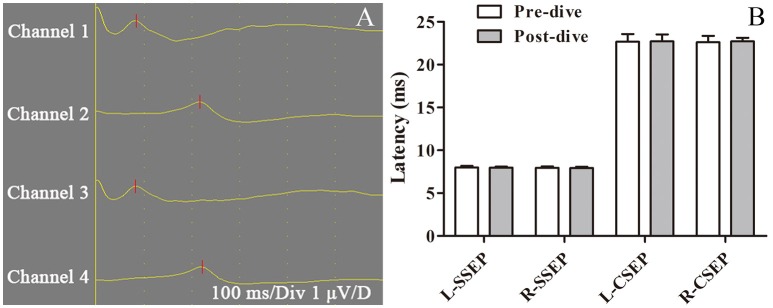
Figure 8.
Sensory evoked potential in a swine DCS model. Sensory evoked potential (SEP) was tested pre-dive and 6 h post-dive in 11 swine following a simulated air dive to 40 m for 35 min with an 11 min decompression. First lumbar vertebra and head were selected to collect electroneurographic signals from right and left ankles, which were defined as spinal somatosensory evoked potential (SSEP, channels 1 and 3) and cortical somatosensory evoked potential (CSEP, channels 2 and 4) (A). Both sides of SSEP and CSEP were compared pre-dive and post-dive, with no significant changes (B).