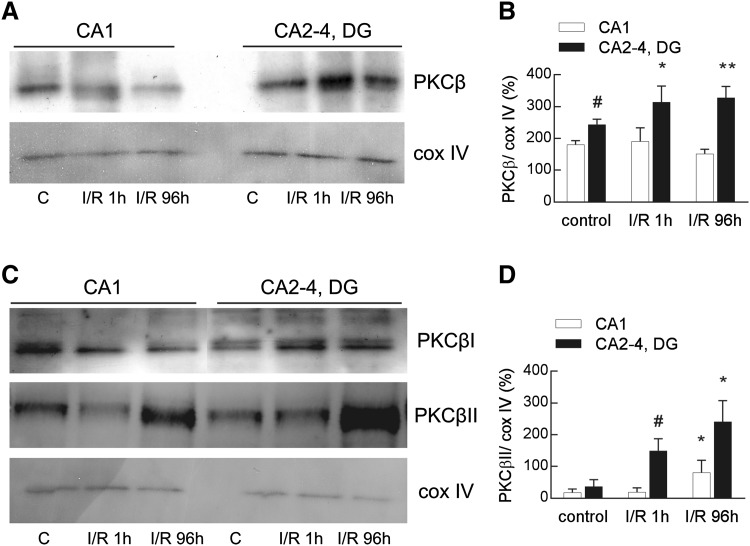
Fig. 1.
Ischemia/reperfusion-induced changes in total PKCβ and PKCβII immunoreactivity in the mitochondrial fraction isolated from the ischemia-vulnerable (CA1) and ischemia-resistant (CA2-4, DG) parts of the hippocampus. Hippocampi were obtained from control and ischemic animals subjected to 5 min ischemia and 1 or 96 h of reperfusion (I/R 1 h and I/R 96 h). The pure mitochondrial fractions (20 µg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and analyzed by western blot with anti-PKCβ or anti-PKCβI and βII and anti-cox IV to assess the gel loading. a The immunoblot showing total PKCβ immunoreactivity in the mitochondrial fraction is representative of five independent experiments. b Densities of PKCβ bands were evaluated and data are expressed as a percentage of cox IV (mean ± SD, n = 5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus control CA2-4, DG, #p < 0.05 versus control CA1. c The representative immunoblots of four independent experiments show PKCβI and βII immunoreactivity in the mitochondrial fraction. d Densities of PKCβII bands were evaluated and data are expressed as a percentage of cox IV (mean ± SD, n = 4). *p < 0.05 versus I/R 1 h, #p < 0.01 versus control