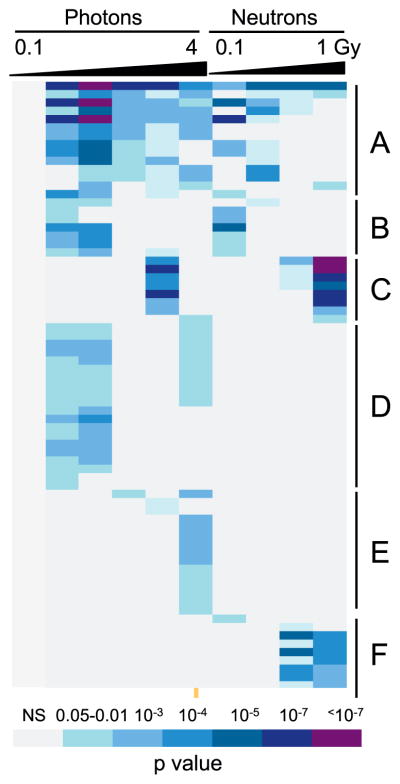
FIG. 2.
Gene ontology analysis of differentially expressed genes by dose. GO terms broadly represented across doses after both photon and neutron irradiations (panel A) were dominated by TP53 signaling and apoptosis functions. Similar functions were also seen among GO terms significant only at lower doses of both radiation qualities (panel B). Terms significant only at higher doses of both radiations (panel C) included NK-cell mediated immunity and glycoproteins. Categories that were only seen as significant after X-ray irradiation (panel D) included additional cell death and apoptosis and DNA repair functions, while those significant only after higher X-ray doses (panel E) included TNF and cell membrane functions, as well as additional apoptotic functions. GO terms that appeared as significant only after neutron exposure (panel F) were related to histones and the nucleosome. An additional 46 GO terms were enriched only among genes differentially expressed after 1 Gy neutrons (see Supplementary Table S2; http://dx.doi.org/10.1667/RR0004CC.1.S2), representing mainly immune-related and additional chromatin functions. The colors represent Benjamini-corrected P values as indicated in the color key; NS= not significant (corrected P > 0.05). The columns represent, from left to right, doses of 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 Gy of X rays, and 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 and 1 Gy of neutrons. A fully-annotated version is available in Supplementary Table 2.