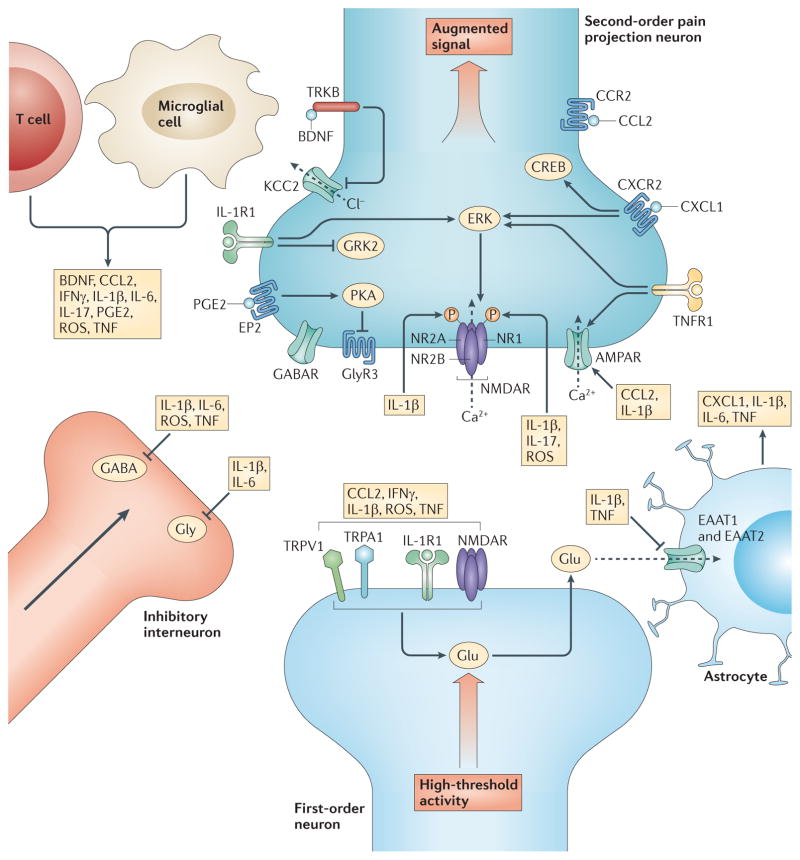
Figure 3. Neuroimmune enhancement of nociception.
Soluble mediators released by reactive immunocompetent cells in the central nervous system diffuse and bind to receptors on presynaptic and postsynaptic terminals in the spinal dorsal horn to modulate excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission, resulting in nociceptive hypersensitivity. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), CC-chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), reactive oxygen species (ROS) and interferon-γ (IFNγ) increase glutamate (Glu) release from central terminals, partly due to the activation of transient receptor potential channel subtypes (TRPV1 and TRPA1), and functional coupling between interleukin-1 receptor 1 (IL-1R1) and presynaptic ionotropic glutamate receptors (NMDAR). TNF, IL-1β, IL-6 and ROS decrease GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) and glycine (Gly) release by inhibitory interneurons. IL-1β and CCL2 also increase AMPA (α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole proprionic acid) signalling, and TNFR1 signalling increases the expression of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors (AMPARs). TNF increases NMDAR activity through the phosphorylation (P) of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), while IL-17 and ROS induce phosphorylation of the NR1 receptor subunit in spinal cord neurons. IL-1β increases the calcium permeability of NMDAR through activation of SRC family kinases and also via phosphorylation of the NR1, NR2A and NR2B subunits. CXCL1 signalling via CXCR2 induces rapid activation of neuronal ERK and CREB. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signalling via TRKB downregulates the potassium-chloride cotransporter KCC2, increasing the intracellular Cl− concentration and weakening the inhibitory GABAA and glycine channel hyperpolarization of second-order nociceptive projection neurons. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) signalling at the EP2 receptor activates protein kinase A (PKA), thereby inhibiting glycinergic neurotransmission via GlyR3. IL-1R1 signalling reduces neuronal expression of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2), a negative regulator of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), including chemokine and prostaglandin receptors, leading to sustained neuronal GPCR signalling. TNF and IL-1β downregulate astrocyte expression of the Glu transporters excitatory amino acid transporter 1 (EAAT1) and EAAT2, leading to enhanced glutamatergic transmission. CCR2, CC-chemokine receptor 2; GABAR, GABA receptor.