Fig. 6.
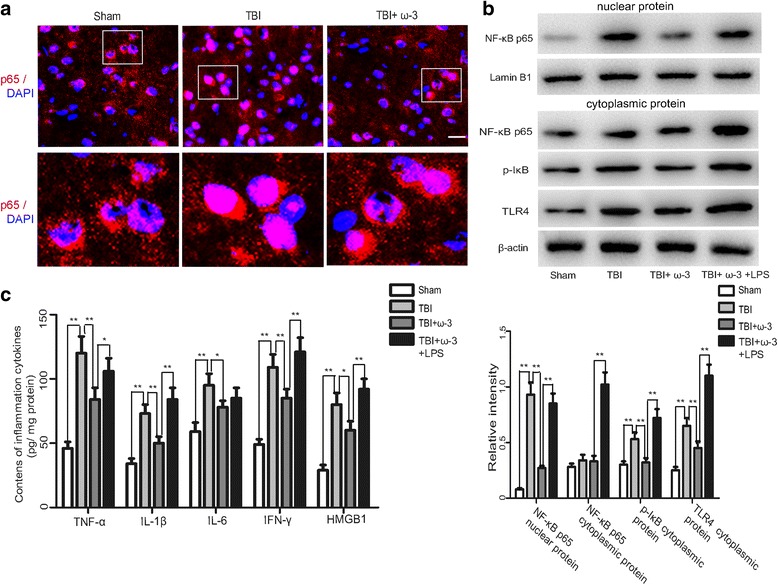
ω-3 PUFA supplementation inhibits HMGB1-mediated activation of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway in lesioned cortices. a ω-3 PUFA supplementation inhibited NF-κB p65 translocation to the nucleus (p < 0.05). Representative photomicrographs of HMGB1 staining in the experimental groups. b The expression of HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB-related factors (NF-κB p65, p-IκB, and TLR4) increased 3 days after TBI (p < 0.05). Subsequent ω-3 PUFA supplementation inhibited NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation and decreased the expression of NF-κB p65, p-IκB, and TLR4. The inhibitory effect of ω-3 PUFA supplementation on the TLR4/NF-κB pathway was reversed by the TLR4 agonist, LPS (p < 0.05). c The inhibitory effect of ω-3 PUFA supplementation on the neuroinflammatory response was also reversed by LPS (p < 0.05); n = 6 in each group. The values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, scale bars = 50 μm
