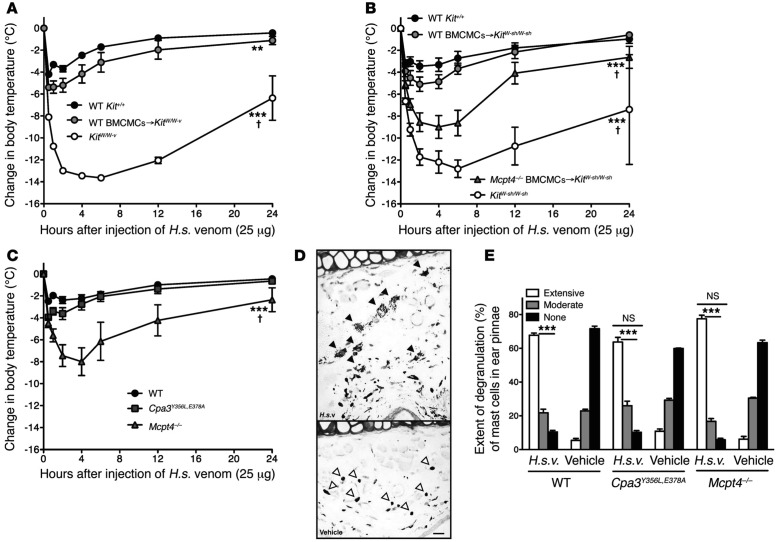
Fig. 2.
Mast cells can diminish Heloderma suspectum venom (H.s.v.)–induced hypothermia and mortality through mast cell protease 4–dependent mechanisms. Changes in rectal temperatures after intradermal injection of H.s.v. (25 mg in 20 ml Dulbecco Modified Eagle Medium [DMEM] solution) into the ear pinnae (one ear pinna of each mouse) of: (A) wild-type (WT) WBB6F1-Kit+/+, mast cell-deficient WBB6F1-KitW/W-v, and WT BMCMCs→KitW/W-v mice (i.e., WBB6F1-KitW/W-v mice which had been engrafted, 6 to 8 weeks before venom challenge, in one ear pinna with 2 million bone marrow–derived cultured mast cells (BMCMCs) derived from WT WBB6F1-Kit+/+ mice) (the death rates of Kit+/+, WT BMCMCs→KitW /W-v, and KitW /W-v mice within 24 hours after H.s.v. injection were 0% [0/21], 7% [1/15, P = 0.42 vs. Kit+/+ mice], and 65% [13/20, P <0.0001 vs. Kit+/+ mice], respectively); (B) WT C57BL/6-Kit+/+, mast cell–deficient C57BL/6-KitW-sh/W-sh, WT BMCMCs→KitW-sh/W-sh, and Mcpt4-/- BMCMCs→KitW-sh/W-sh mice (the death rates of Kit+/+, WT BMCMCs→KitW-sh/W-sh, Mcpt4-/- BMCMCs→KitW-sh/W-sh, and KitW-sh/W-sh mice within 24 hours after H.s.v. injection were 5% [1/19], 11% [2/18, P = 0.48 vs. Kit+/+ mice], 43% [6/14, P = 0.01 vs. Kit+/+ mice], and 50% [10/20, P = 0.006 vs. Kit+/+ mice], respectively); or (C) WT C57BL/6-Kit+/+ mice, C57BL/6-Cpa3Y356L,E378A mice (which have a catalytically inactive CPA3) and C57BL/6-Mcpt4-/- mice (the death rates of Kit+/+, Cpa3Y356L,E378A, and Mcpt4-/- mice within 24 hours after H.s.v. injection were 7% [1/15], 0% [0/14, P = 0.52 vs. Kit+/+ mice], 40% [6/15, P = 0.007 vs. Kit+/+ mice], respectively). Each figure shows data pooled from at least three independent experiments with each group of mice (n = 2-5 mice per group per each individual experiment). **P <0.01, ***P <0.001 versus WT WBB6F1-Kit+/+ or WT C57BL/6-Kit+/+ mice; †P <0.01~0.001 versus each other group (A–C). (D) Extensive degranulation of mast cells (some indicated by closed arrowheads) 1 hour after intradermal injection of H.s.v. (25 mg in 20 ml DMEM), but not vehicle (DMEM) alone (mast cells without evidence of degranulation are indicated by open arrowheads) in WT C57BL/6 mice (Toluidine blue stain; scale bar: 50 µm). (E) Degranulation of mast cells 60 minutes after intradermal injection of H.s.v. (25 mg in 20 ml DMEM) or vehicle (DMEM) alone in WT C57BL/6, Mcpt4-/-, or Cpa3Y356L,E378A mice (injection was into one ear pinna of each mouse). ***P <0.001 versus corresponding vehicle-injected groups; NS = not significant (P >0.05) versus values for WT mice. [This is a reproduction of Figure 1 from Akahoshi M, Song CH, Piliponsky AM, et al. Mast cell chymase reduces the toxicity of Gila monster venom, scorpion venom, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in mice. J Clin Invest 2011;121:4180-91 (reference 18), reprinted with the permission of the publisher, the American Society for Clinical Investigation.]