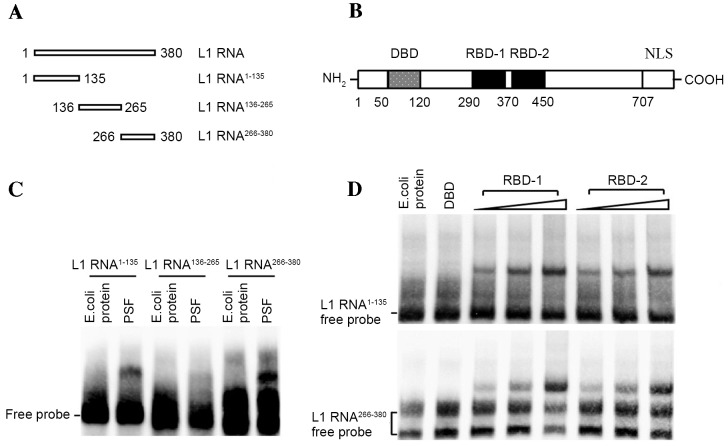
Figure 2.
Identification of interacting domain of PSF protein and L1 RNA. (A) Sub-fragments of L1 RNA. (B) PSF structural domains. (C) Binding of PSF protein to three fragments of L1 RNA separately by EMSA. Total E. coli protein was used as the protein negative control. (D) Identification of the binding of the DBD, RBD-1 and RBD-2 of PSF to L1 RNA1–135 (upper panel) and L1 RNA266–380 (lower panel) by EMSA. Total E. coli protein was used as the control protein. PSF, polypyrimidine tract-binding protein-associated splicing factor; L1, long interspersed nuclear element 1; E. coli, Escherichia coli; EMSA, electrophoretic mobility shift assay; DBD, DNA binding domain; RBD, RNA binding domain; NLS, nuclear localization signal.