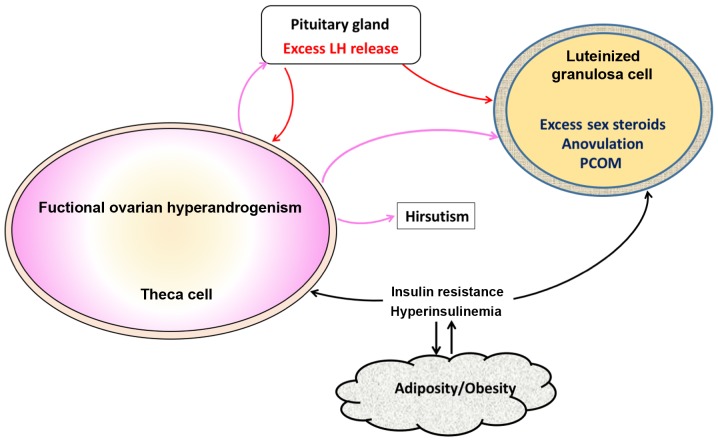
Figure 2.
Pathological events in PCOS. Ovarian hyperandrogenism is very common in PCOS and contributes to several abnormalities including hirsutism, oligo-anovulation, and PCOM. LH secretion from pituitary gland is needed for the ovarian androgen production, but other factors such as hyperinsulinism and obesity are also necessary for full-blown pathogenesis of PCOS. Insulin resistance, which is very common in PCOS leads to hyperinsulinemia, which stimulates theca cells and aggravates hyperandrogenism. Excess insulin along with androgen, luteinize granulosa cells prematurely. Adipogenesis is another abnormality resulting from hyperinsulinism. Elevated androgens coming from theca cells in turn stimulate pituitary and cause LH excess, which worsens hyperandrogenism. These changes in granulosa cells further exacerbate PCOM and lead to oligo-anovulation. PCOS, polycystic ovary syndrome; PCOM, polycystic ovarian morphology; LH, luteinizing hormone.