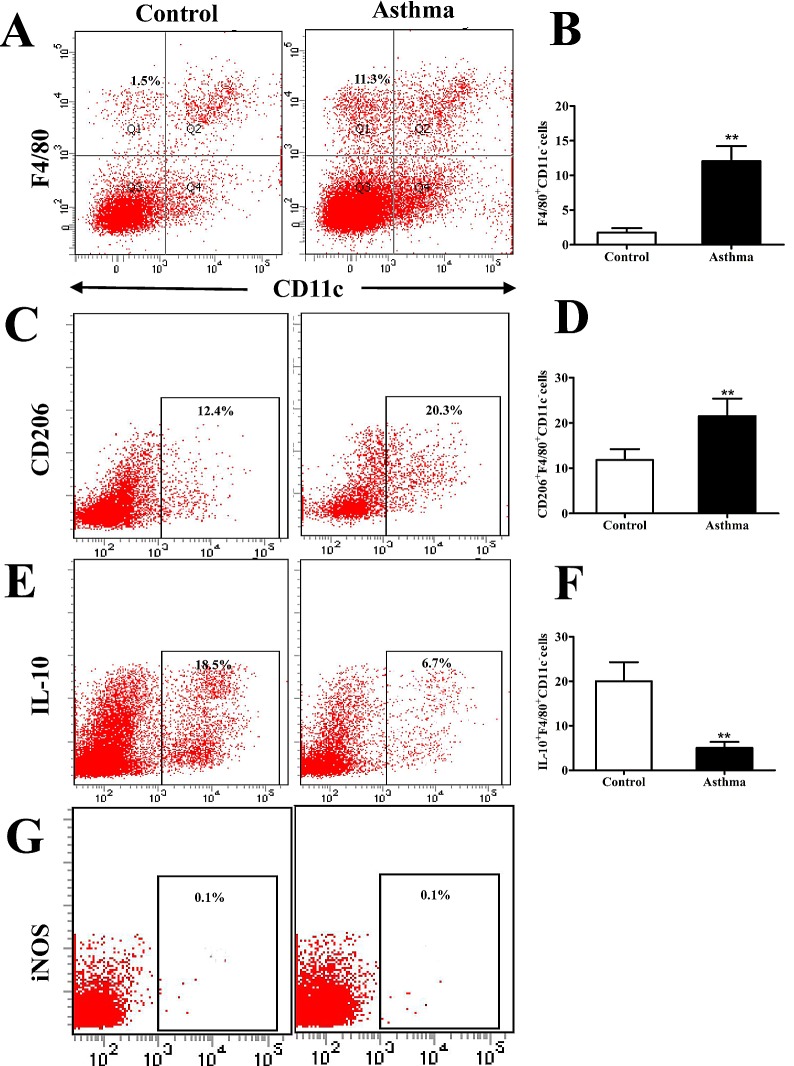
Figure 1.
Flow cytometry analysis of CD206+F4/80+CD11c− cells in the lungs of OVA-induced asthmatic mice. (A) Flow cytometry was used to identify F4/80+ and CD11c− lung IMs isolated from the lungs of OVA-induced asthmatic mice and PBS-treated control mice. Boxes indicate the gating region of lung IMs (F4/80+CD11c−; gate B). (B) Relative percentages of F4/80+CD11c− cells in control and OVA-induced asthmatic mice. (C) Detection of lung IMs positive for the cell surface marker CD206. Boxes indicate the gating region of CD206+F4/80+CD11c− cells (gate C). (D) Relative percentages of CD206+F4/80+CD11c− cells in control and OVA-induced asthmatic mice. (E) Detection of lung IMs positive for IL-10. Boxes indicate the gating region of IL-10+F4/80+CD11c− cells (gate C). (F) Percentages of lung IMs expressing IL-10 in control and OVA-asthmatic mice (G) Detection of lung IMs positive for iNOS. Boxes indicate the gating region of iNOS+F4/80+CD11c− cells (gate P2). Percentages on each dot plot represent positively stained cells. All data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, n=6. **P<0.01 vs. control. CD, cluster of differentiation; F4/80, epidermal growth factor family cell surface antigen; IM, interstitial macrophages; IL-10, interleukin-10; OVA, ovalbumin; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PE-cy5, phycoerythrin-cyano 5 dye; FITCH, fluorescein isothiocyanate.