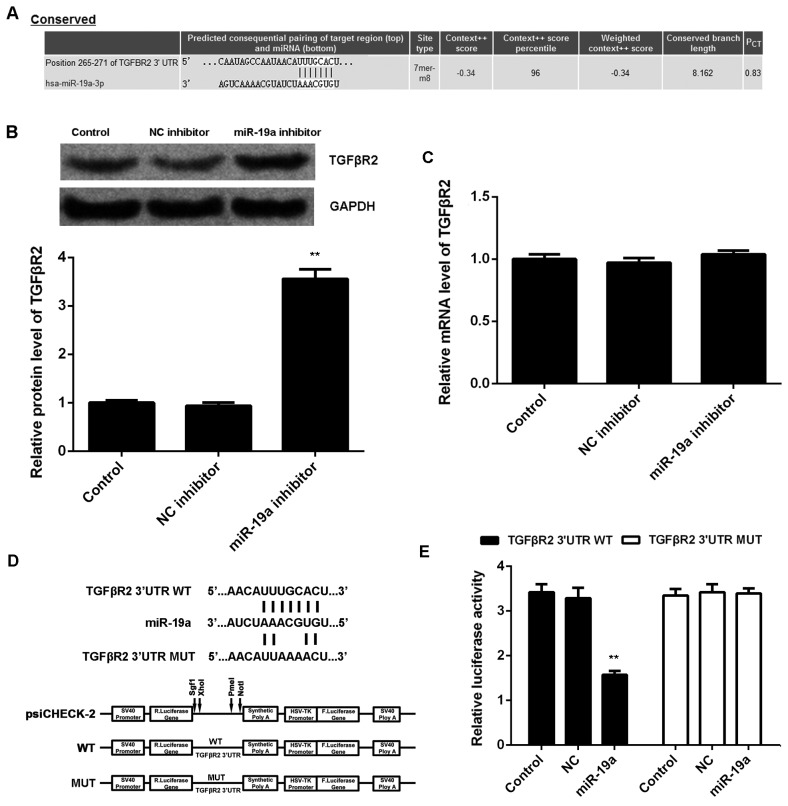
Figure 3.
TGFβR2 is a target of miR-19a. (A) TargetScan software demonstrated that TGFβR2 was a putative target of miR-19a, and their targeting relationship was evolutionally conserved. (B) Western blotting and (C) reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction were used to examine the protein and mRNA expression levels of TGFβR2 in C666-1 cells transfected with NC inhibitor or miR-19a inhibitor, respectively, relative to GAPDH. Non-transfected cells were used as the Control. (D) The fragment of TGFβR2 3′UTR containing the putative binding sites of miR-19a was amplified and subcloned into the psiCHECK-2 vector downstream of the luciferase gene sequence, named TGFβR2 3′UTR WT. The 3′UTR of TGFβR2 containing MUT binding sites of miR-19a was generated and also subcloned into the psiCHECK-2 vector downstream of the luciferase gene sequence, named TGFβR2 3′UTR MUT. (E) Luciferase activity was measured in C666-1 cells co-transfected with TGFβR2 3′UTR WT or TGFβR2 3′UTR MUT with miR-19a mimic or NC miR. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. **P<0.01 vs. the Control. TGFβR2, transforming growth factor β receptor 2; miR, microRNA; NC, negative control; UTR, untranslated region; WT, wild type; MUT, mutant.