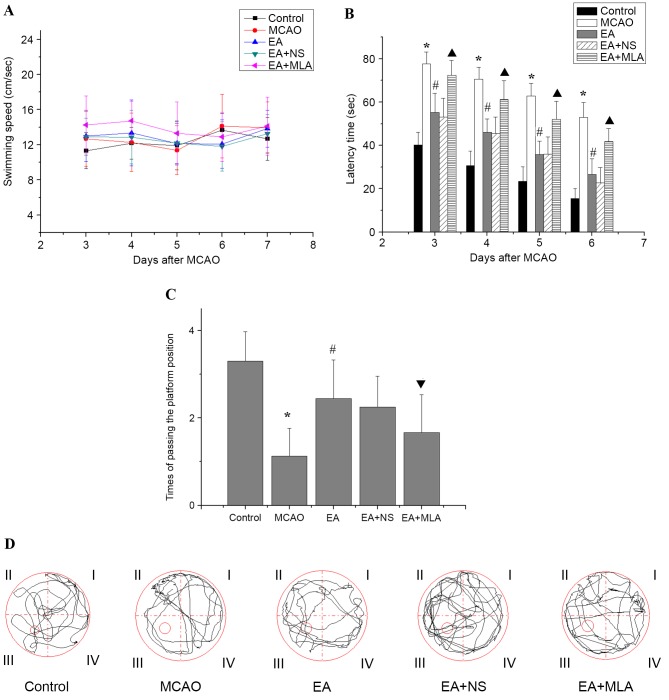
Figure 1.
Effects of EA on the learning and memory of transient focal cerebral ischemic injured rats in the water maze. (A) No significant differences in swimming speed were observed among the control (n=10), MCAO (n=8), EA (n=9), EA + NS (n=9) and EA+ MLA (n=9) groups up to day 7. (B) The latency time to reach the hidden platform, (C) the number of times the rats passed the platform position and (D) typical traces during the test. *P<0.01 vs. control, #P<0.01 vs. MCAO, ▲P<0.01 vs. EA + NS and ▼P<0.05 vs. EA + NS. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean. EA, electroacupuncture; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; NS, normal saline; MLA, methyllycaconitine.