Fig. 2.
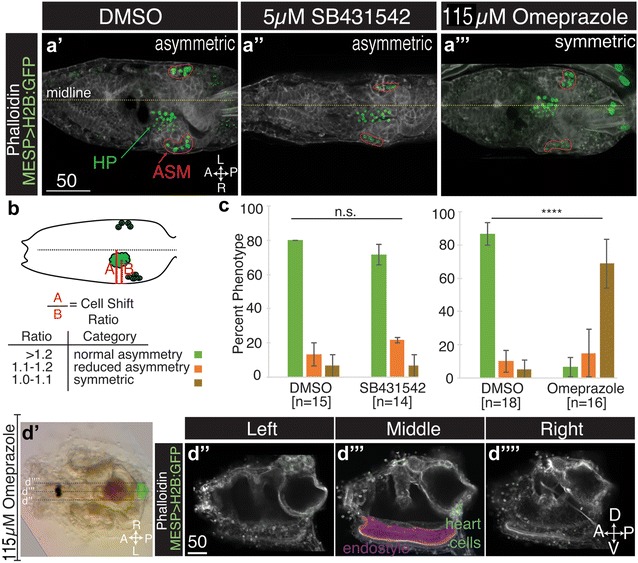
Ion flux is required for laterally asymmetric heart positioning. a′–a‴ Ventral projections of transgenic Stage 31 larva, and heart founder lineage cells are demarcated by Mesp > H2B:GFP (green), including heart precursors (HP) and atrial siphon muscle precursors (ASM). a′–a‴ Typical asymmetric heart precursor positioning in DMSO controls (a′), larva treated with 5 µM SB431542 (a″) or larva treated with 115 µM omeprazole (a‴). b Schematic illustrating cell shift ratio used for scoring heart precursor positioning, as detailed in the “Methods” section. c Graphical representation of larval heart position data. Error bars represent SEM, and n represents total number of larva scored over three-independent trials. Chi-square test derived P values comparing control and omeprazole-treated larva (p = 2.9E−5) or SB431542-treated samples (p = 0.84). d′–d′′′′ Dorsal view (d′) and lateral sections (d″–d′′′′) of Ciona juveniles displaying a midline heart phenotype following omeprazole treatment. In (d′), the heart is false-colored green and the endostyle is false-colored purple. In lateral sections (d″–d′′′′), heart cell nuclei are labeled by Mesp > H2B:GFP. In all images, anterior is to the left. All scale bars are in micrometers
