Fig. 6.
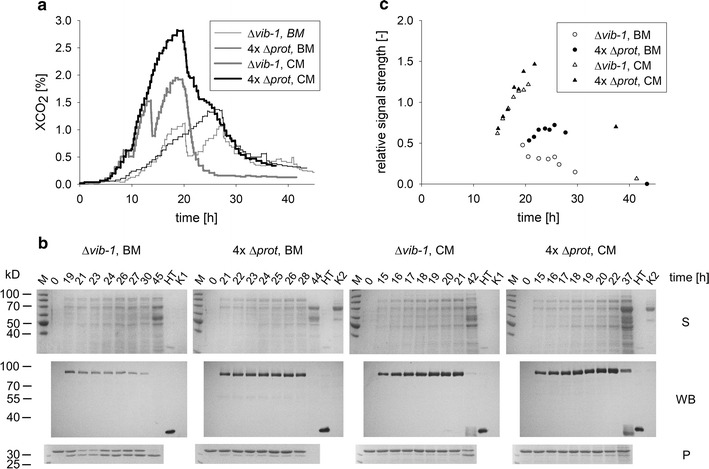
Fourfold protease deletion results in higher protein yields due to lower protease activity. a Exhaust gas composition as a representative value for the growth characteristics. Cultivation was conducted in a parallel bioreactor system in minimal Bird medium (BM) and complex medium (CM). The employed strains were ∆vib-1 (DHN-252: Pccg1nr-glat-ht186-10×his, exo-1, ∆vib-1, ∆vvd) and 4×∆prot (DHN-270: Pccg1nr-glat-ht186-10xhis, exo-1, ∆spr-7, ∆apr-9, ∆apr-3, ∆NCU00263). b Analysis of heterologous protein production. Proteins from the supernatant (not concentrated) were separated via SDS-PAGE (S) and the product was detected after Western blot transfer (WB). The signal was visualized directly on the membrane with an NBT/BCIP system. The protease assay (P) was performed as mentioned above. c Yield quantification via Western blot analysis. Band intensities in b were quantified via image processing software and ratios calculated in relation to HT186-D11 (HT, 25 ng) produced in E. coli. As a negative control, strains with an exo-1, Δvib-1 background (K1, strain DHN-141) and exo-1 (K2, strain FGSC #2256) were used (no production strains)
